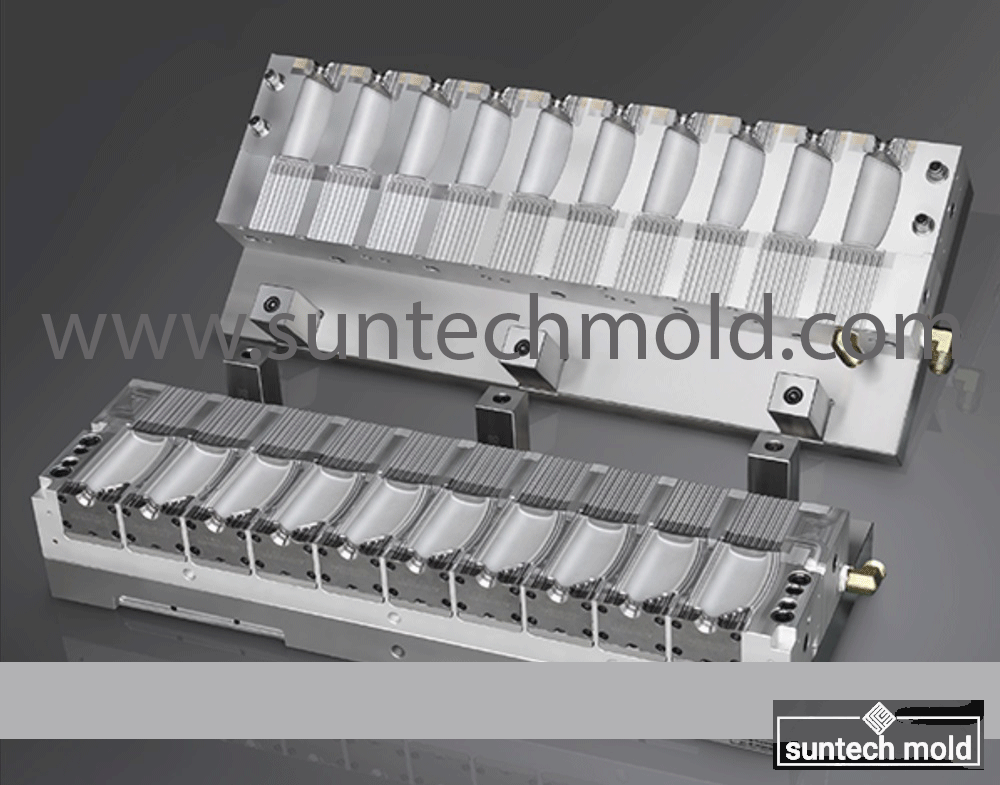
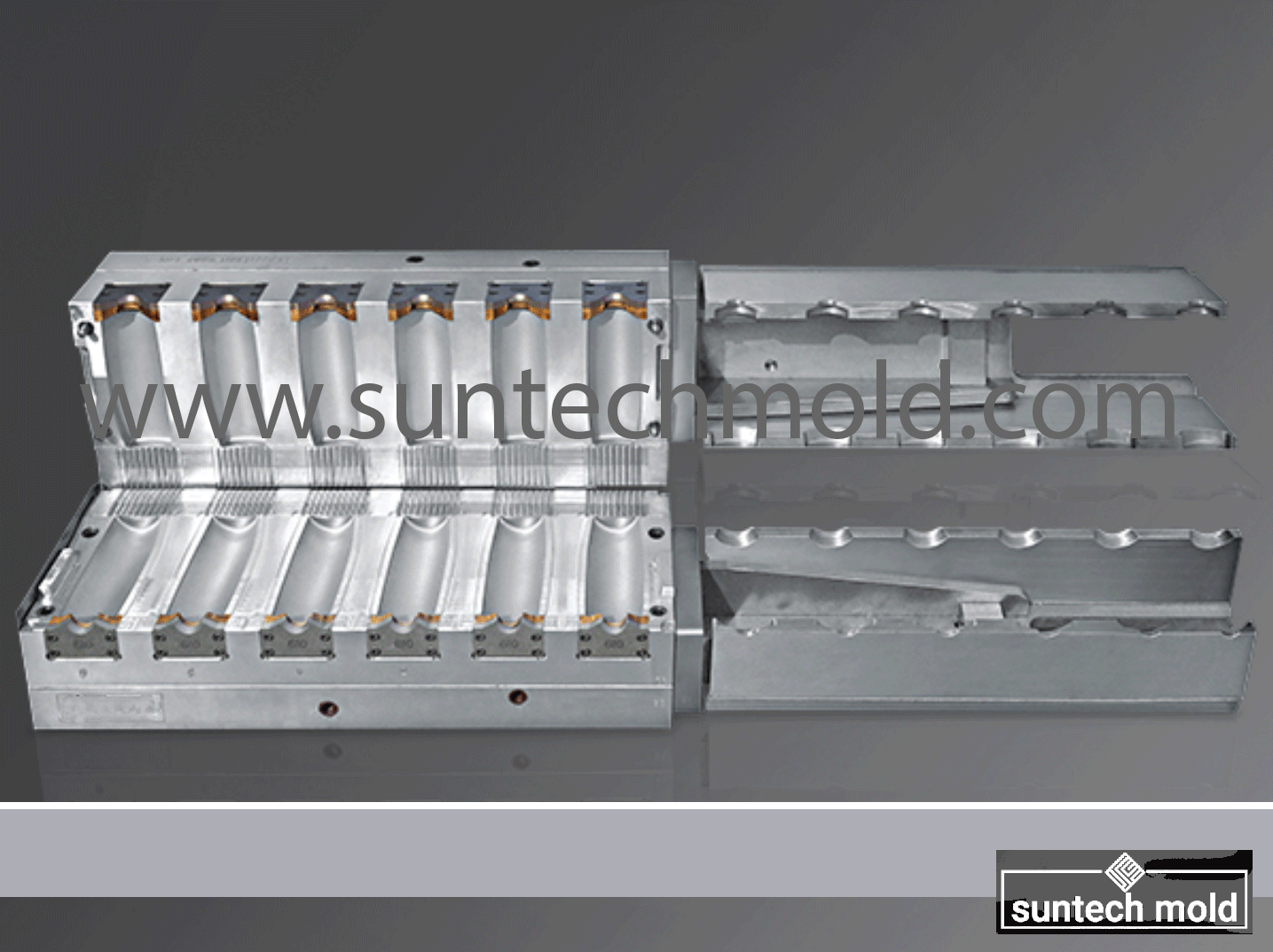
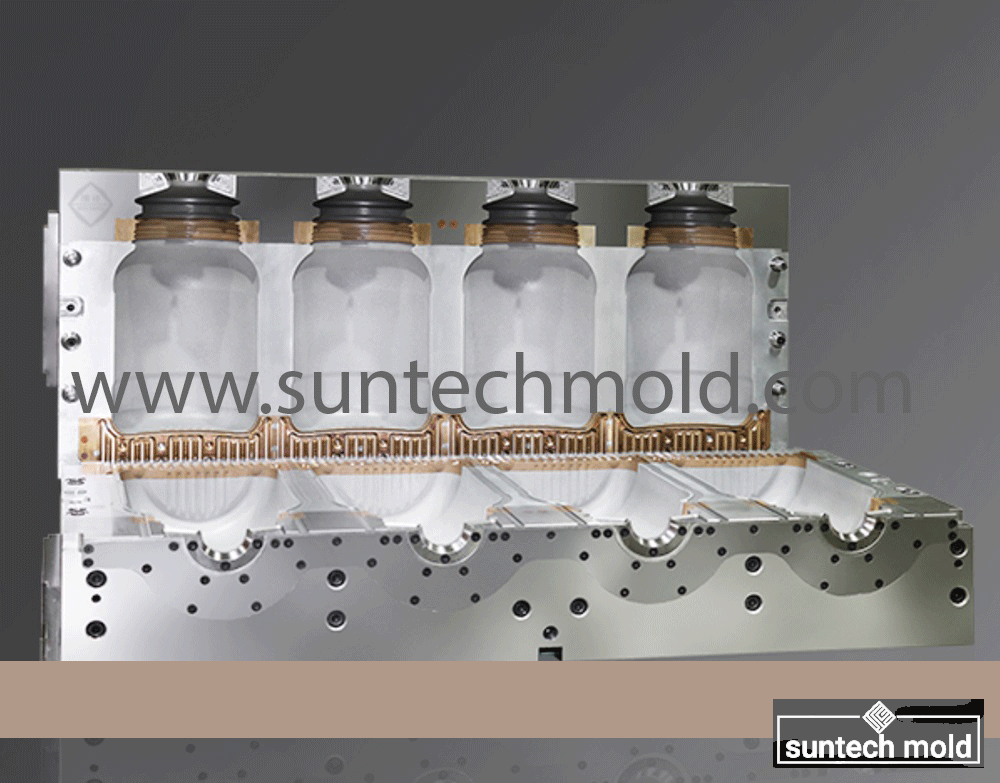
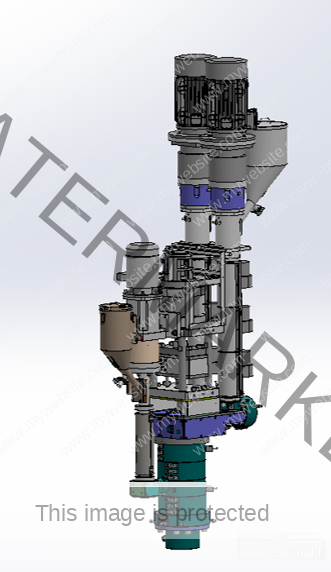
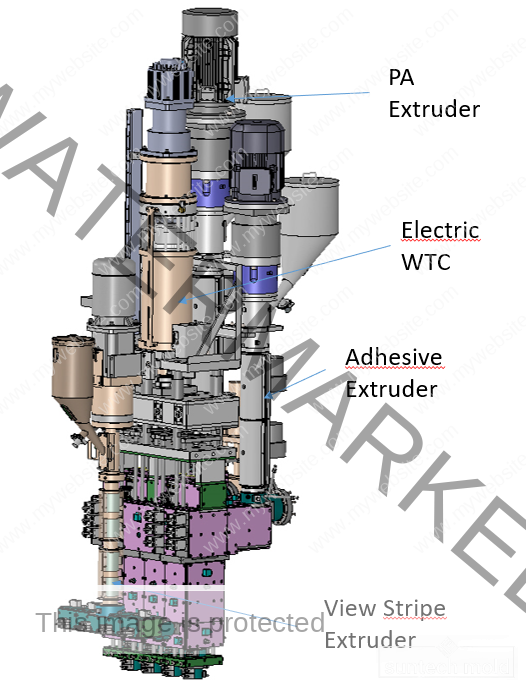
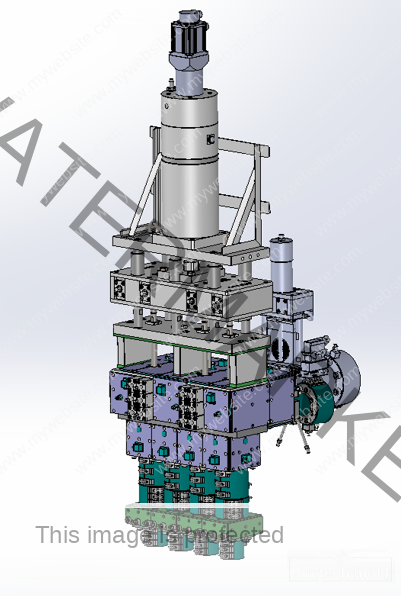
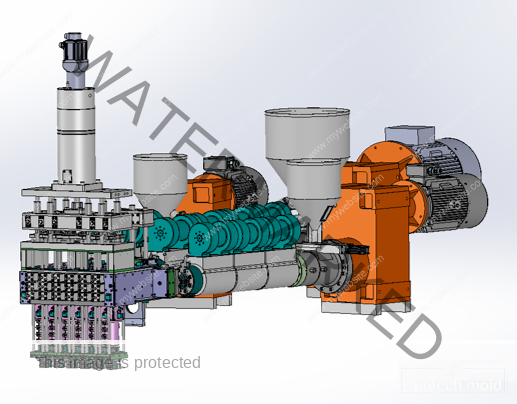
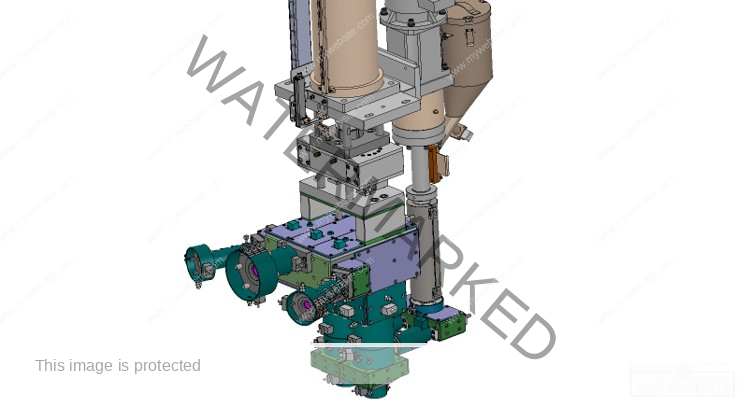
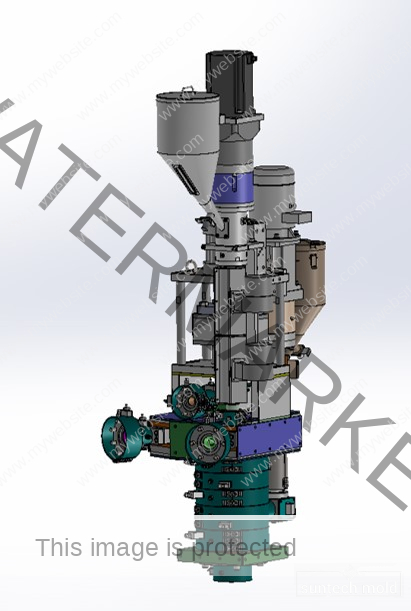
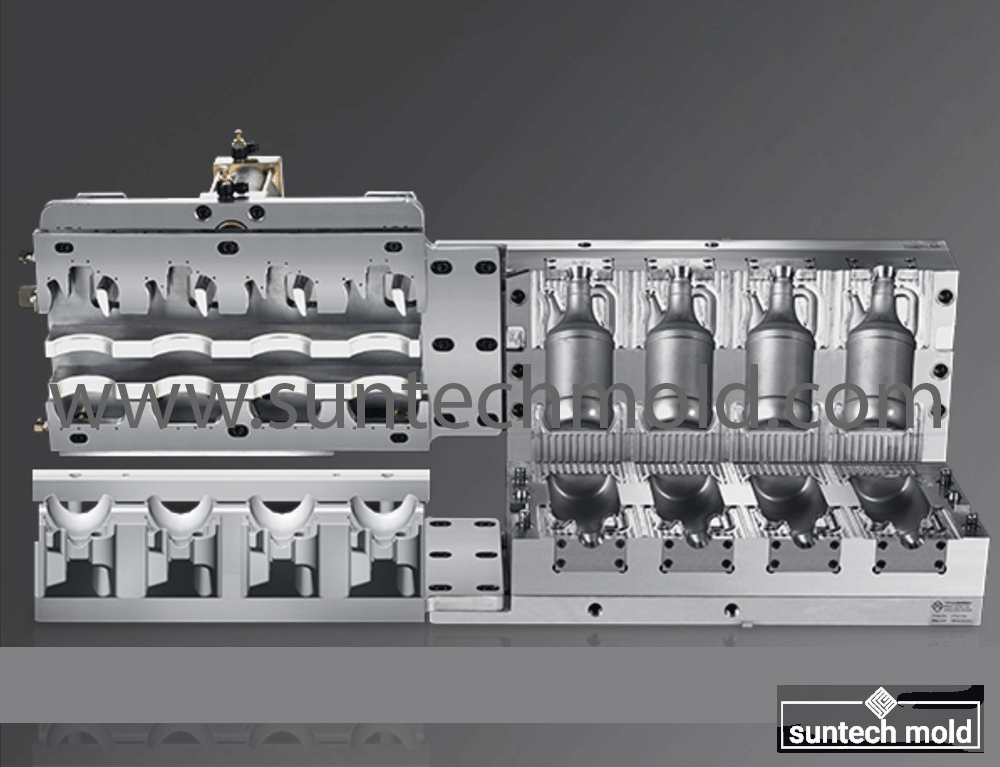
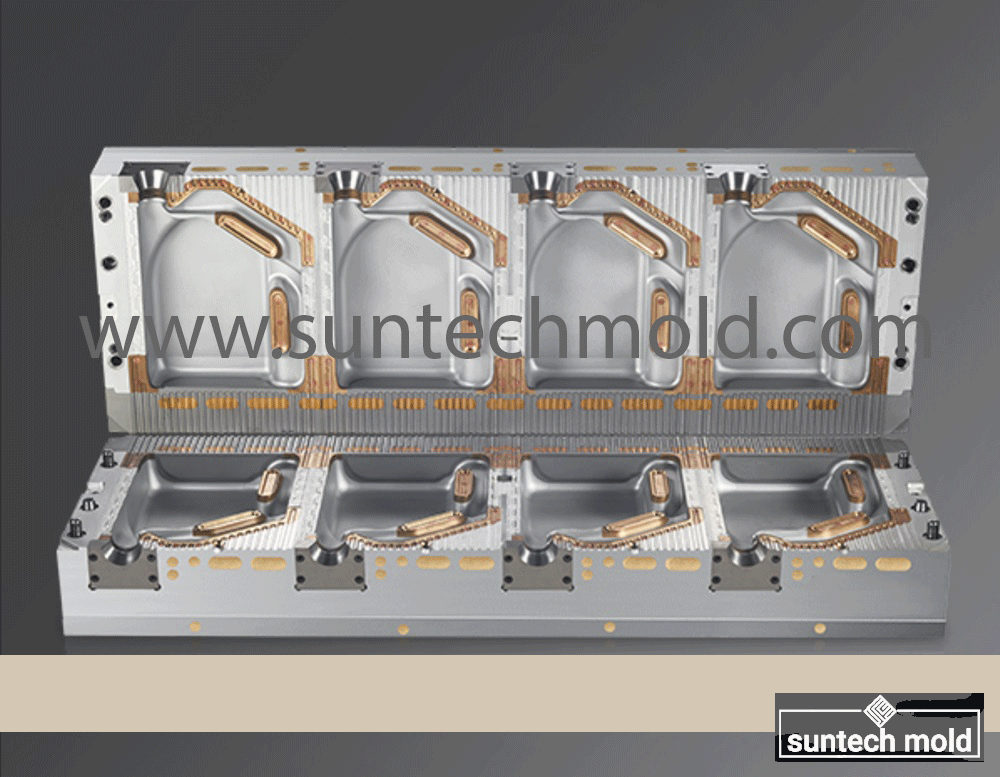
2 Cavities 5L Engine Oil Mold – Precision Cooling for High-Volume Production
The 2 cavities 5L engine oil mold is a high-performance solution designed for manufacturers producing large-format lubricant bottles with precision and efficiency. Engineered with cutting-edge cooling technology and optimized geometry, this mold is perfect for high-output environments where quality, speed, and consistency are essential.
Built to accommodate the rigorous demands of the blow molding industry, this mold integrates advanced cooling channels to deliver uniform temperature control, faster cycle times, and exceptional product consistency.
Why Choose Our 2 Cavities 5L Engine Oil Mold?
Choosing the right mold for producing 5-liter engine oil bottles can significantly impact your production speed, product quality, and operational efficiency. Our 2 cavities 5L engine oil mold provides two high-precision cavities, enabling balanced production and increased throughput without compromising structural integrity or finish quality.
Key Features:
-
Two synchronized mold cavities for high-efficiency output
-
Integrated cooling channels for optimized thermal management
-
Durable materials such as H13 tool steel or 7075 aluminum
-
Uniform wall thickness and precise neck finishes
-
Compatible with HDPE, PP, and other industrial-grade resins
Smart Cooling Design for Superior Performance
Efficient cooling is at the core of every high-quality blow mold. The 2 cavities 5L engine oil mold features a highly engineered internal cooling system that ensures fast, even cooling across all surfaces. This not only reduces cycle times but also enhances the final bottle’s dimensional stability.
Cooling Channel Geometry
Proper channel geometry plays a vital role in thermal regulation.
-
Optimized Shapes: Curved and serpentine channel paths allow better coolant circulation and heat dissipation.
-
Balanced Diameter: Channels are designed with precise diameters to ensure effective coolant flow without excessive pressure drop.
Placement and Layout
-
Even Distribution: Cooling channels are evenly positioned throughout the mold to maintain consistent temperatures.
-
Hot Spot Targeting: Extra cooling near high-heat zones ensures fast and uniform solidification of the plastic.
Thermal Conductivity & Flow Dynamics
A mold’s thermal behavior significantly impacts production efficiency. Our mold leverages high-conductivity materials and strategic cooling design to maintain precise temperature control.
Flow Rate and Dynamics
-
Optimal Flow Rates: Each cavity is designed to ensure coolant flow is uninterrupted, avoiding dead zones or stagnant areas.
-
Simulation Tested: Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations are used to validate cooling performance before production.
High-Conductivity Materials
-
Copper Inserts & Channels: Enhancing heat transfer in key zones.
-
Aluminum & Tool Steel Base: Selected for strength and thermal efficiency.
Engineered for Durability and Maintenance
The 2 cavities 5L engine oil mold isn’t just about performance—it’s also built to last. Every component is tested for longevity, easy maintenance, and minimal downtime.
Pressure & Expansion Considerations
-
Reinforced Structures: Withstand internal pressure from coolant without deformation.
-
Thermal Expansion Compensation: Designed to prevent cracking or warping under high temperatures.
Maintenance and Inspection
-
Accessible Layout: Cooling channels are easy to clean and inspect.
-
Inspection Ports: Included for ongoing monitoring of internal systems.
Versatile Compatibility and Customization
This mold is designed for seamless integration with most blow molding machines and can be tailored to your specific production requirements.
Custom Options Include:
-
Handle styles and neck finish variations
-
Embossing or debossing for branding
-
Adaptability to different resins and machine types
Whether you’re producing for automotive, industrial, or commercial markets, our 2 cavities 5L engine oil mold offers the flexibility you need to meet diverse production goals.
Sustainable and Cost-Effective Manufacturing
Our mold’s efficient design reduces cycle time and material waste, improving your bottom line. With faster cooling and fewer defects, you’ll benefit from lower energy consumption and more sustainable production cycles.
Operational Benefits:
-
Shorter Cycle Times
-
Reduced Material Waste
-
Lower Maintenance Costs
-
Longer Mold Life
This makes it a smart investment for manufacturers focused on productivity and sustainability.
Conclusion – A Mold Designed for Modern Manufacturing Needs
The 2 cavities 5L engine oil mold represents the perfect blend of engineering excellence, material science, and production efficiency. With its advanced cooling system, durable construction, and customization capabilities, this mold is ready to meet the demands of today’s fast-paced, high-volume production environments.
Whether you’re upgrading your tooling or launching a new product line, choosing a mold with precision cooling and durable materials can make all the difference. Trust Suntech Mold for world-class performance, expert support, and solutions built to last.
Contact us today to get a custom quote or learn more about our mold design capabilities.