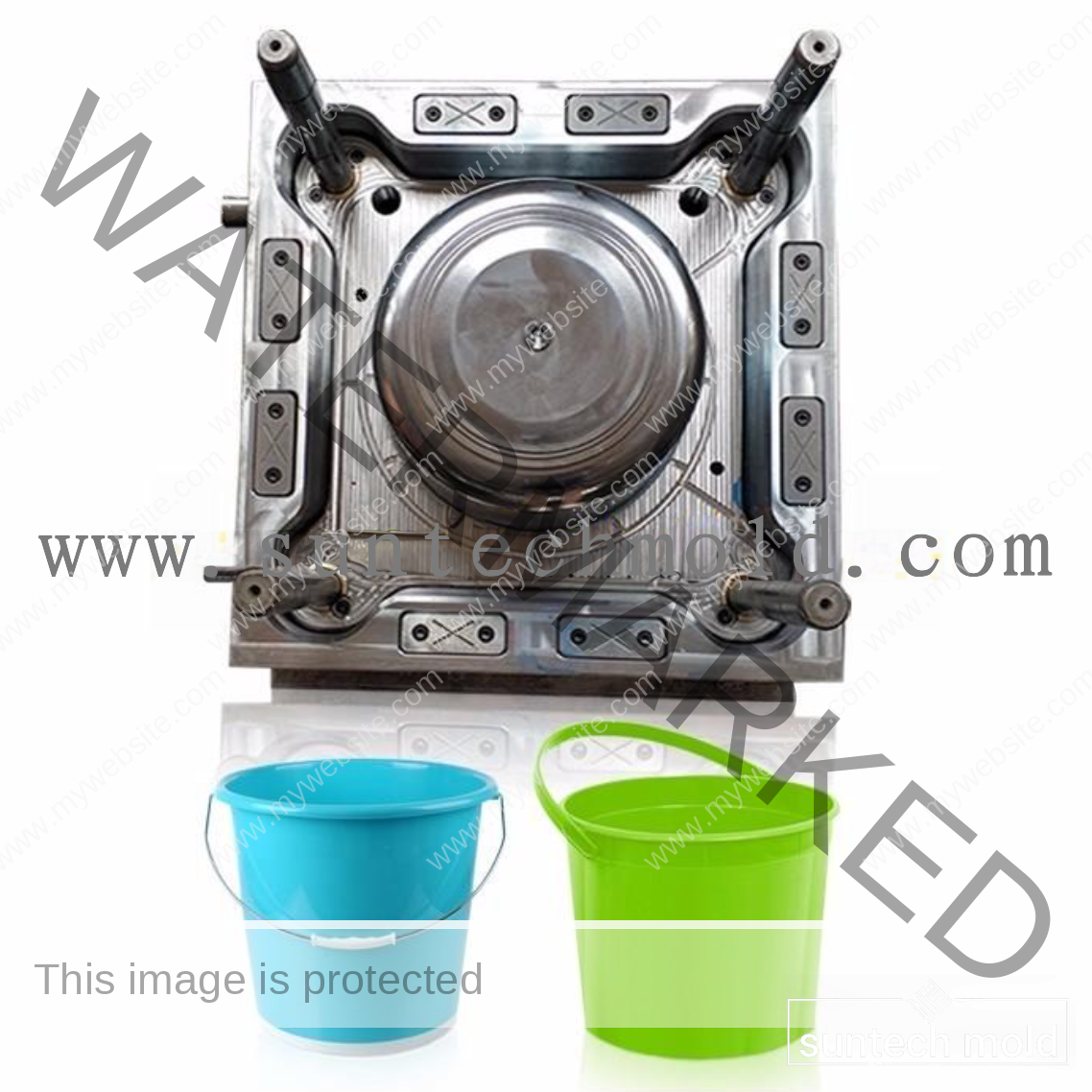
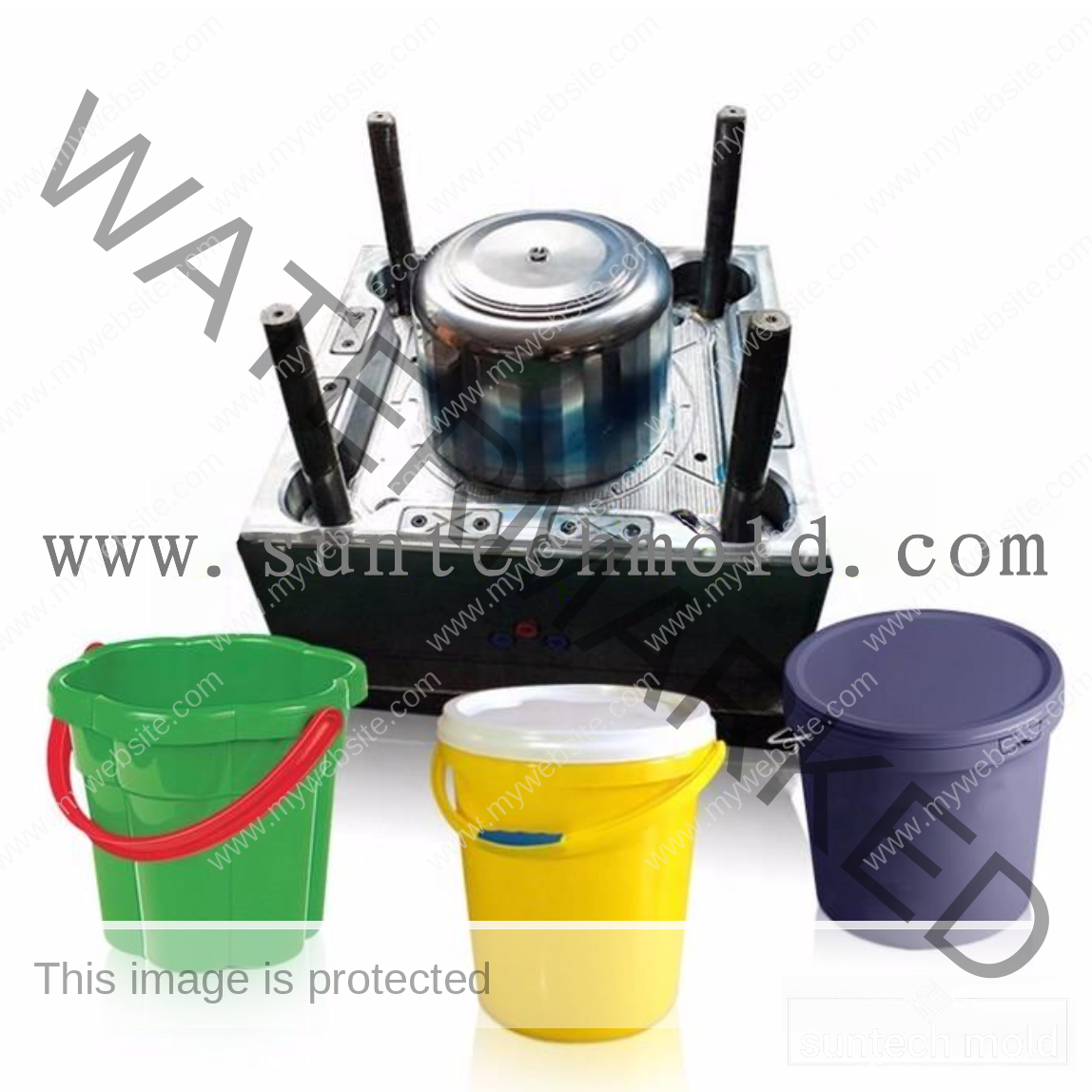
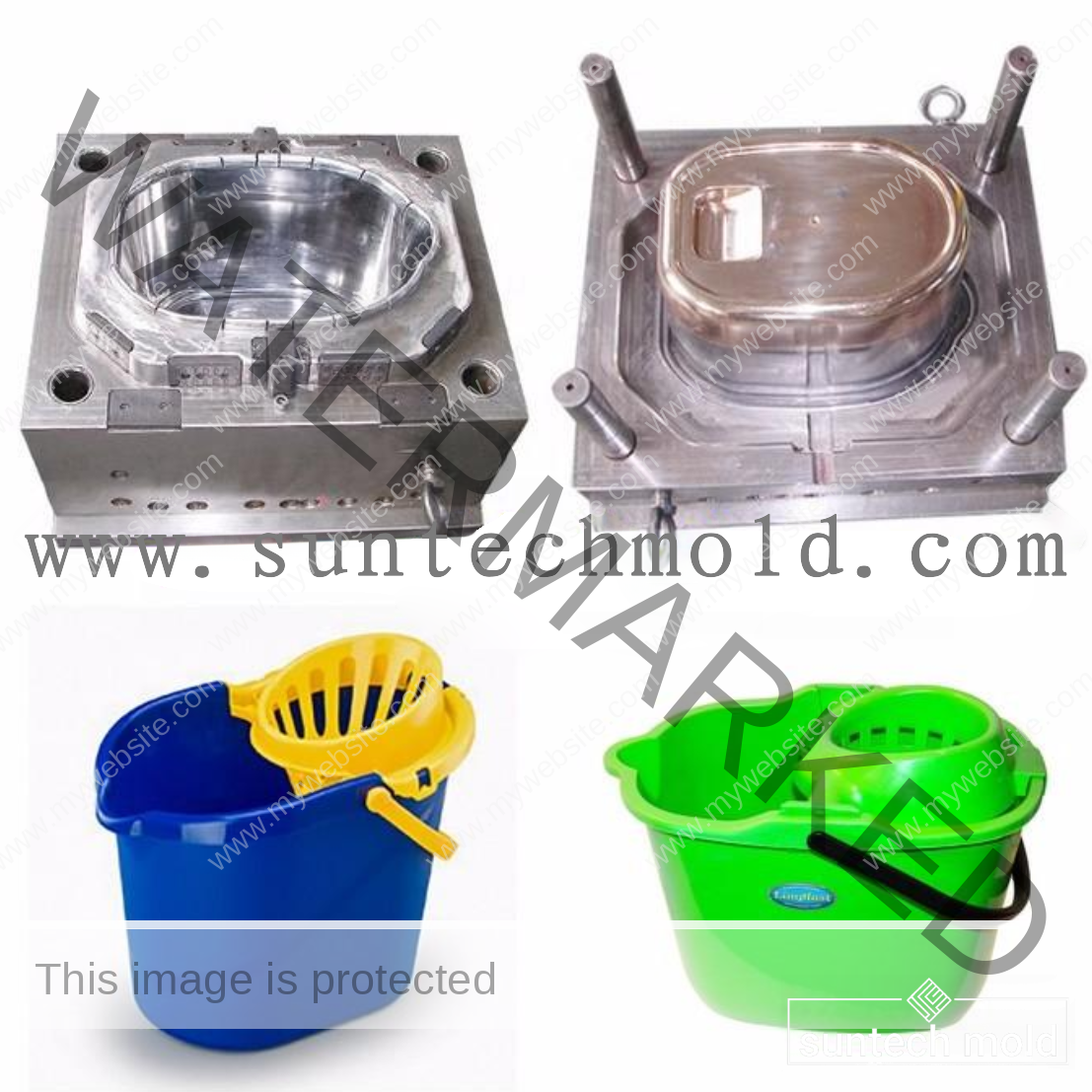
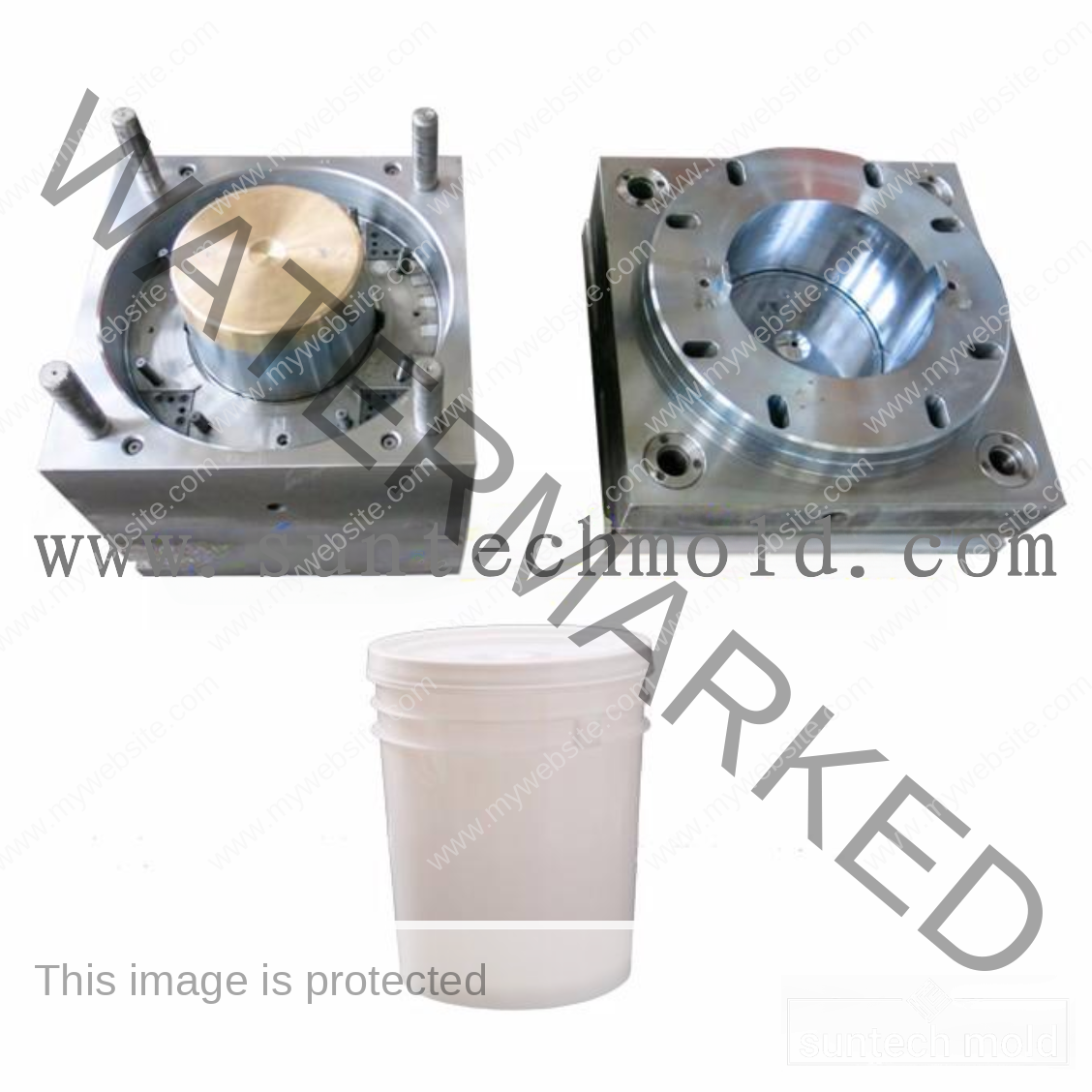
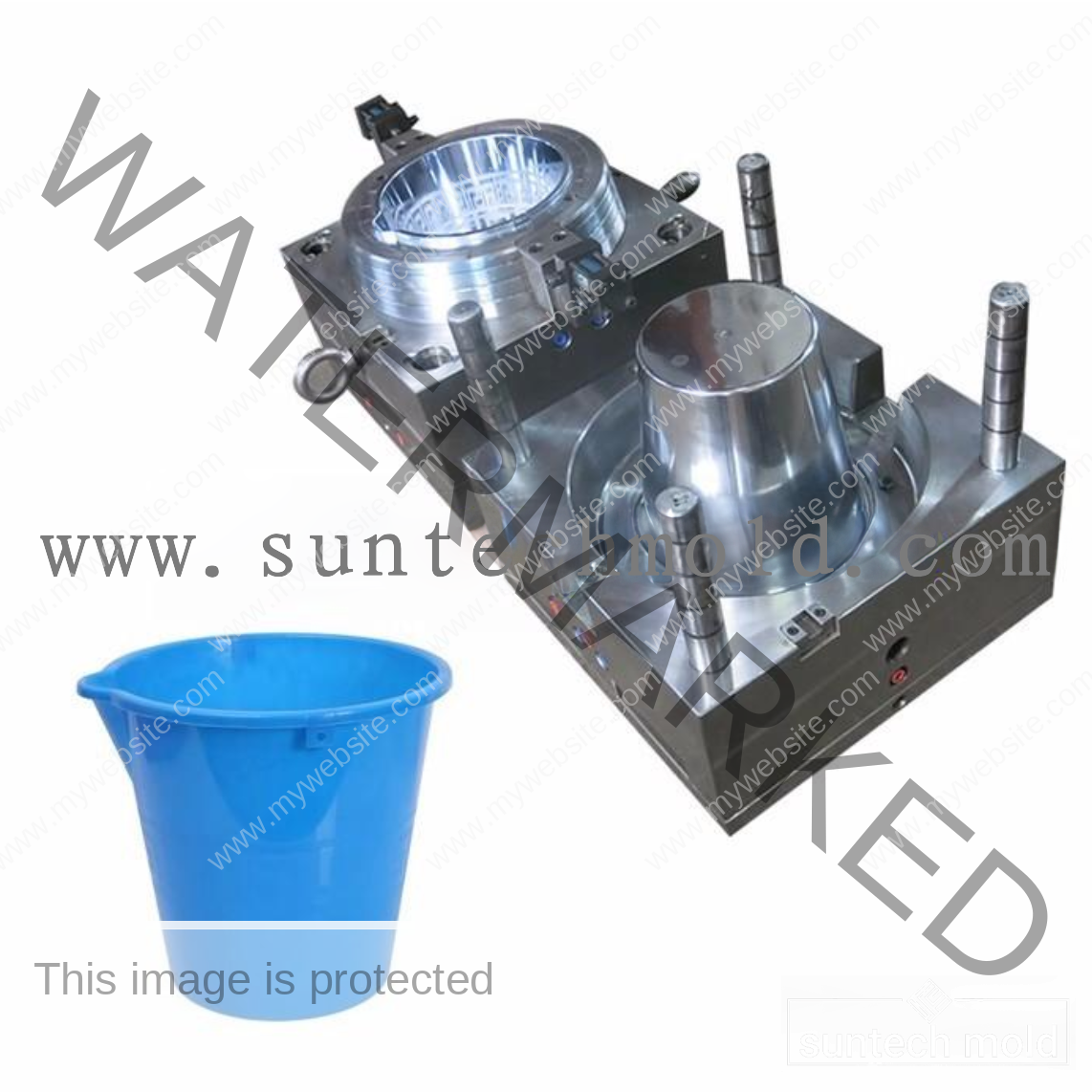
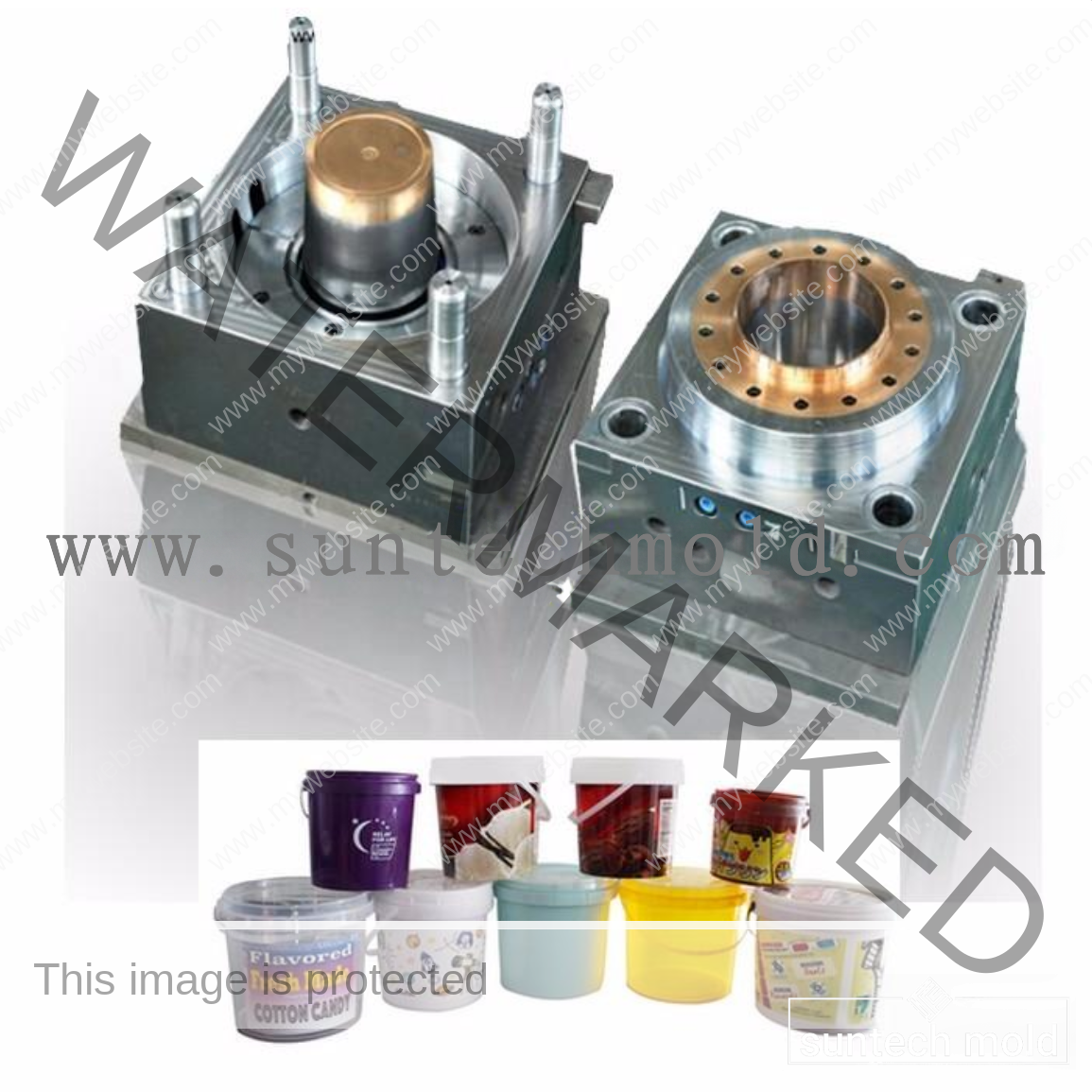
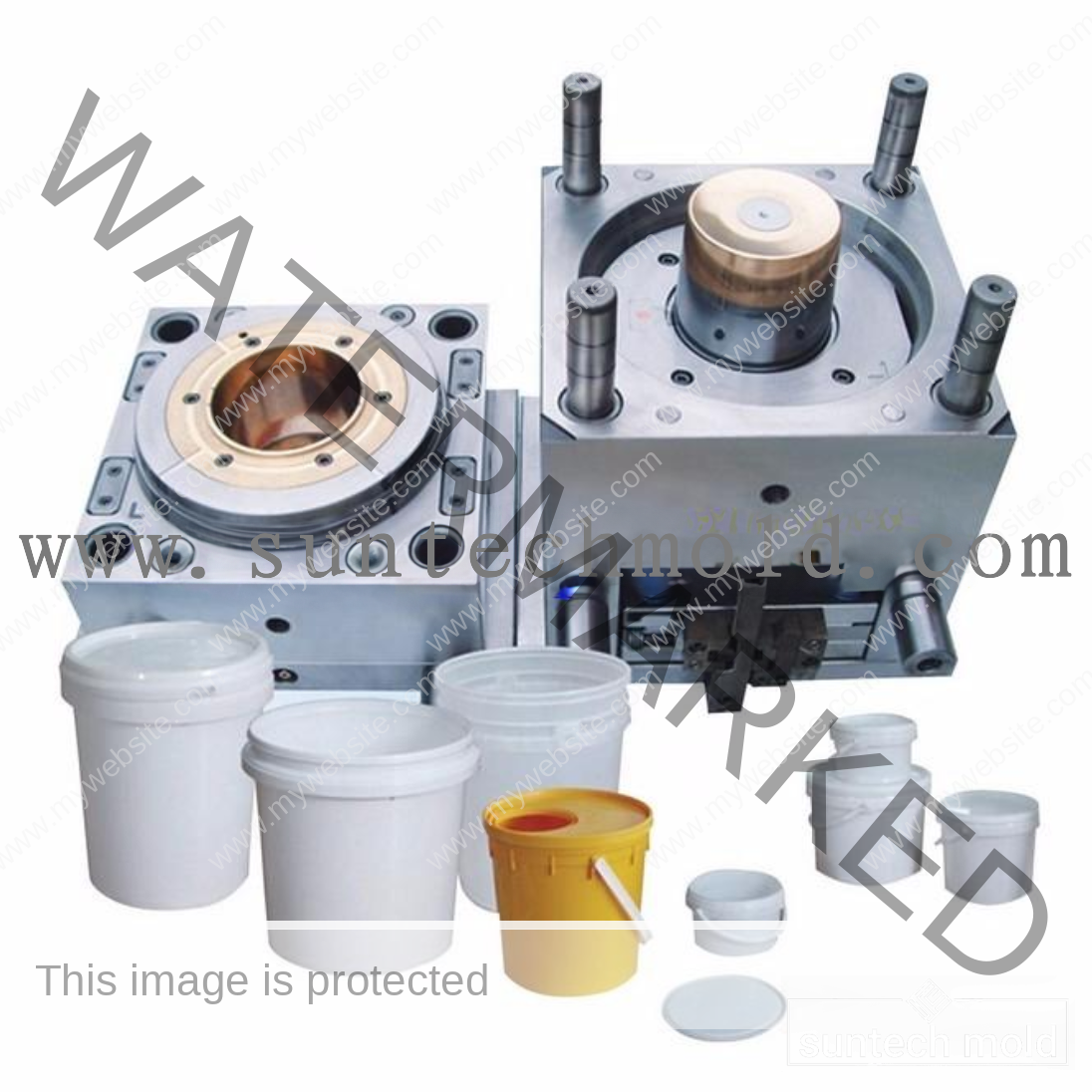
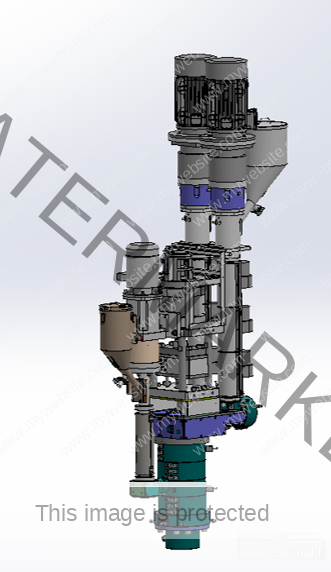
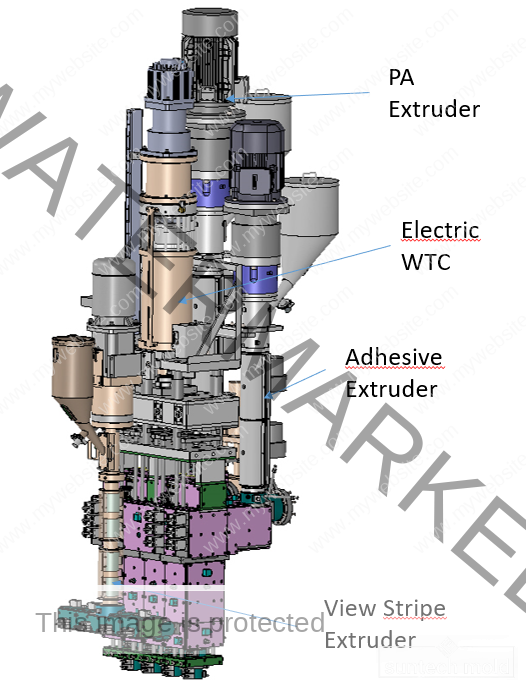
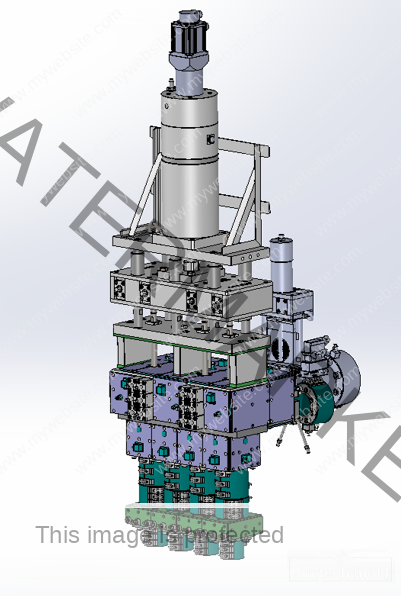
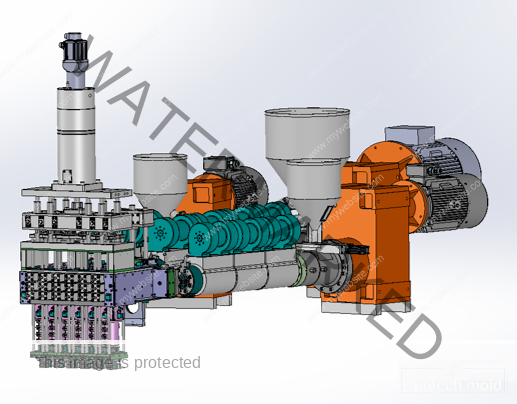
Bucket and Pail Injection Mold
The Bucket and Pail injection mold plays a crucial role in producing durable, high-performance plastic containers for various industrial, commercial, and household applications. Whether you’re manufacturing storage buckets, chemical containers, or food-grade pails, selecting the right mold and materials is essential for quality, durability, and efficiency.
Why Use a High-Quality Bucket and Pail Injection Mold?
Using a premium Bucket and Pail injection mold ensures consistent production, precise dimensions, and strong structural integrity. These molds are designed to handle high-volume manufacturing while delivering consistent product quality and long-term reliability.
Key Benefits:
-
High production efficiency
-
Precise and uniform shapes
-
Minimal material waste
-
Customizable for different sizes and designs
-
Long service life with proper maintenance
Best Materials for Bucket and Pail Injection Mold Applications
Selecting the right material is essential to ensure the end product can withstand its intended use. Below are the most commonly used materials in bucket manufacturing, along with their properties and applications:
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
-
Properties: Excellent impact resistance, strong chemical resistance, UV-stable
-
Applications: Ideal for outdoor and heavy-duty environments
HDPE is widely used for buckets exposed to harsh elements, thanks to its ability to withstand wear and tear.
Polypropylene (PP)
-
Properties: Lightweight, high tensile strength, chemical-resistant
-
Applications: Perfect for food storage and multi-purpose containers
PP is a preferred choice for its versatility and affordability in bucket production.
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
-
Properties: Water-resistant, flexible or rigid, chemical-resistant
-
Applications: Great for liquid or chemical buckets
PVC offers excellent versatility and is ideal for specialized pails requiring moisture resistance.
Beryllium Copper (BeCu)
-
Properties: Superior thermal conductivity, high strength
-
Applications: Mold inserts for faster cooling and better cycle times
BeCu is used in the Bucket and Pail injection mold components to enhance heat dissipation and extend mold life.
Recycled Plastics
-
Properties: Eco-friendly, variable durability
-
Applications: Suitable for green product lines
Using recycled materials supports sustainability efforts without significantly compromising product quality.
Nylon
-
Properties: Abrasion-resistant, durable, high-impact strength
-
Applications: Ideal for heavy-duty buckets under stress
Nylon is used for high-stress applications where strength and endurance are critical.
Elastomers
-
Properties: Flexible, durable, temperature-resistant
-
Applications: Buckets needing elasticity and shape retention
Elastomers offer a unique advantage for specialized pails that require flexibility and stress resistance.
Choosing the Right Bucket and Pail Injection Mold
To ensure your buckets and pails perform well under varying conditions, it’s important to consider the following:
1. Intended Use
Will the bucket be used for food storage, transporting chemicals, or general use? Each application may require different material and mold design specifications.
2. Environmental Conditions
Assess the conditions the bucket will be exposed to, including:
-
UV exposure
-
Moisture
-
Extreme temperatures
These factors can influence the choice of material and mold type.
3. Compliance and Safety
Make sure the materials used in your Bucket and Pail injection mold meet relevant regulatory standards, especially for food-grade or hazardous chemical applications.
Conclusion
Choosing the right Bucket and Pail injection mold involves understanding your application needs, selecting the appropriate materials, and ensuring your molds are built for durability and precision. With the right design and components, manufacturers can produce high-quality buckets and pails that perform reliably across a range of environments.