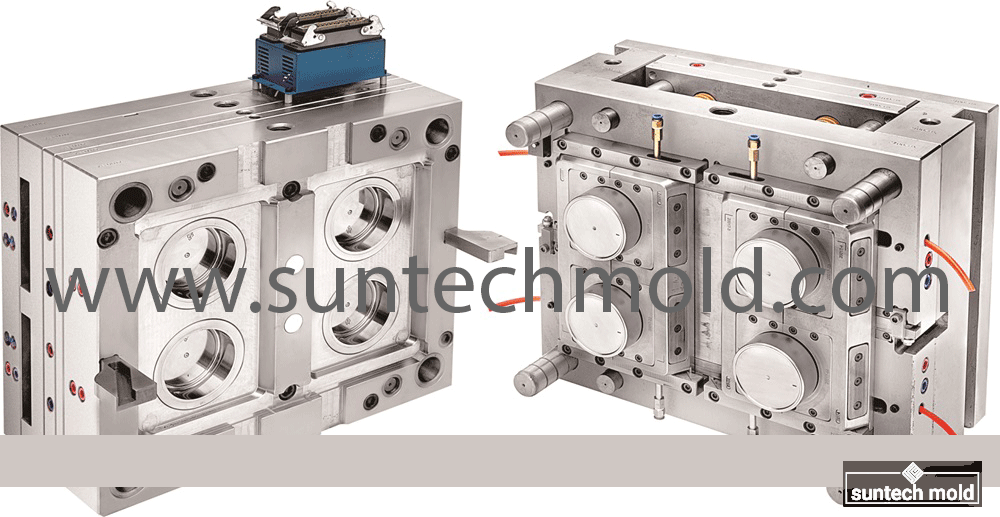
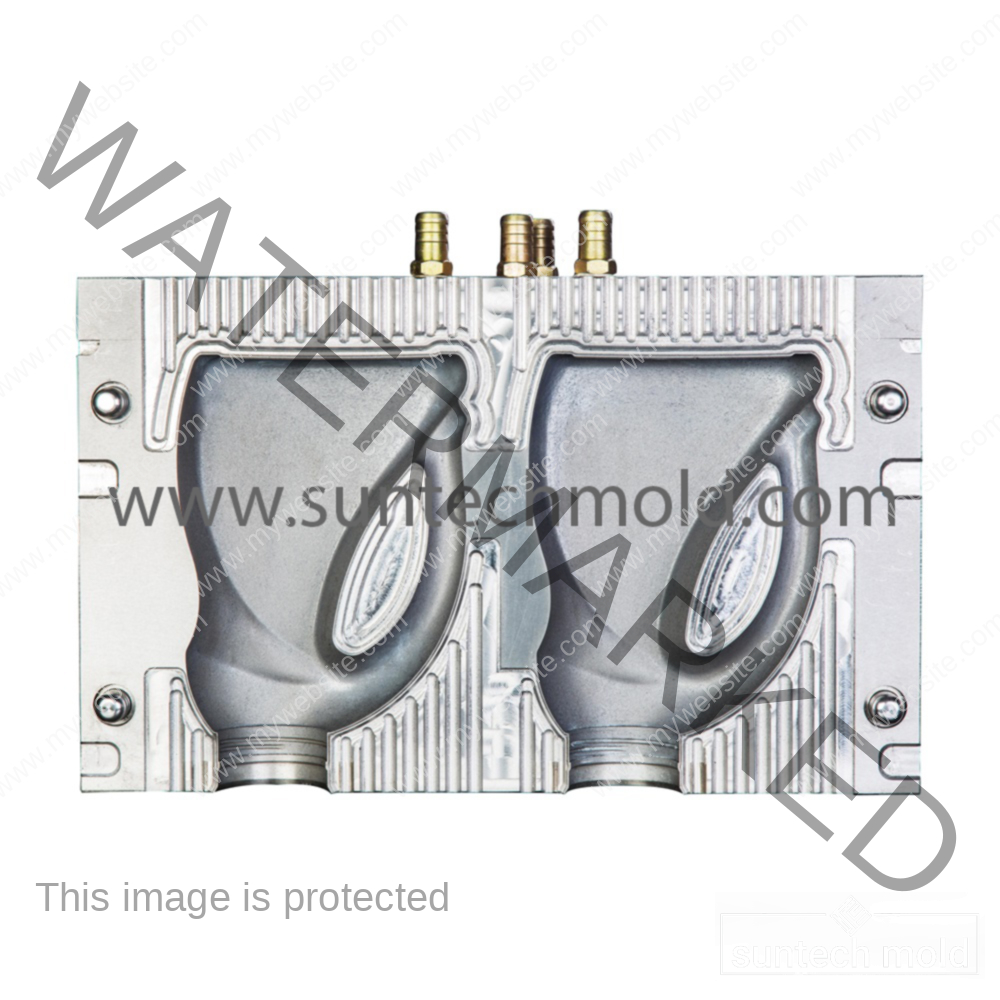
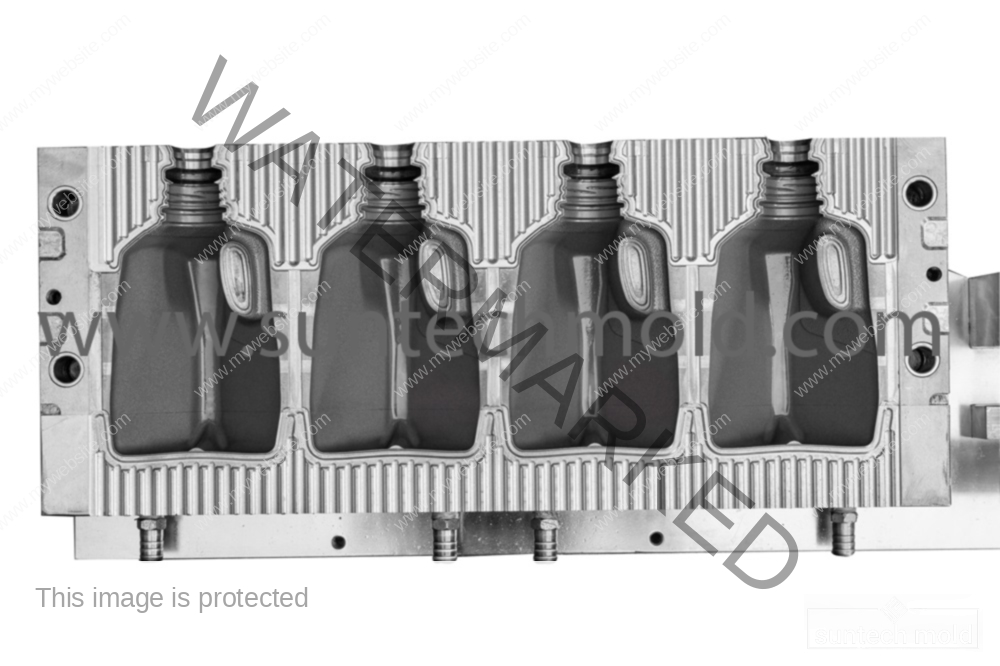
Selecting the right materials for constructing cooling channels in molds is crucial for effective heat transfer and durability. Here are some of the best materials commonly used:
- Steel Alloys
- P20 Steel: Known for its good machinability and toughness, P20 is often used for injection molds and has decent thermal conductivity.
- H13 Steel: This hot work tool steel offers excellent wear resistance and thermal conductivity, making it suitable for high-temperature applications.
- Aluminum Alloys
- 6061 Aluminum: Lightweight with good thermal conductivity, 6061 is easy to machine and can provide efficient cooling.
- 7075 Aluminum: Offers higher strength and is suitable for applications requiring durability, though it can be more challenging to machine.
- Copper Alloys
- C110 Copper: Known for its excellent thermal conductivity, copper is often used in cooling channels where rapid heat transfer is critical.
- Beryllium Copper: Combines high strength with good thermal conductivity, making it suitable for demanding applications.
- Thermally Conductive Plastics
- Polycarbonate: While not as conductive as metals, certain thermally conductive plastics can be used for lightweight applications.
- PPS (Polyphenylene Sulfide): Offers good thermal stability and can be used in specialized cooling applications.
- Composite Materials
- Metal Matrix Composites: These materials combine metals with reinforcing materials to enhance thermal conductivity and strength.
- Carbon Fiber Composites: Although primarily known for strength, some composites can be engineered for thermal conductivity.
- Inconel and Other Superalloys
- Inconel 718: Known for its high strength and oxidation resistance at elevated temperatures, suitable for demanding environments.
- 3D-Printed Materials
- Metal 3D Printing: Additive manufacturing allows for complex cooling channel designs using high-conductivity metals.
- Plastic 3D Printing: Some advanced polymers have good thermal properties and can be used for prototype molds.
Conclusion
When selecting materials for cooling channels, consider factors such as thermal conductivity, machinability, strength, and cost. Often, a combination of materials may be used to optimize performance and durability.