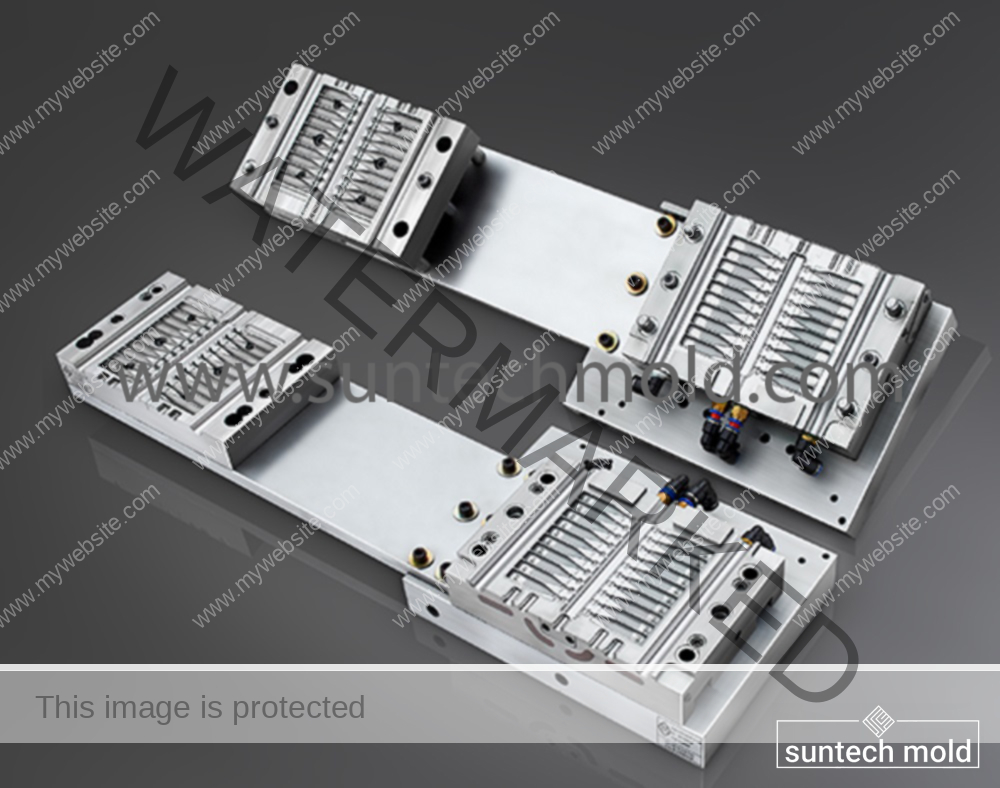
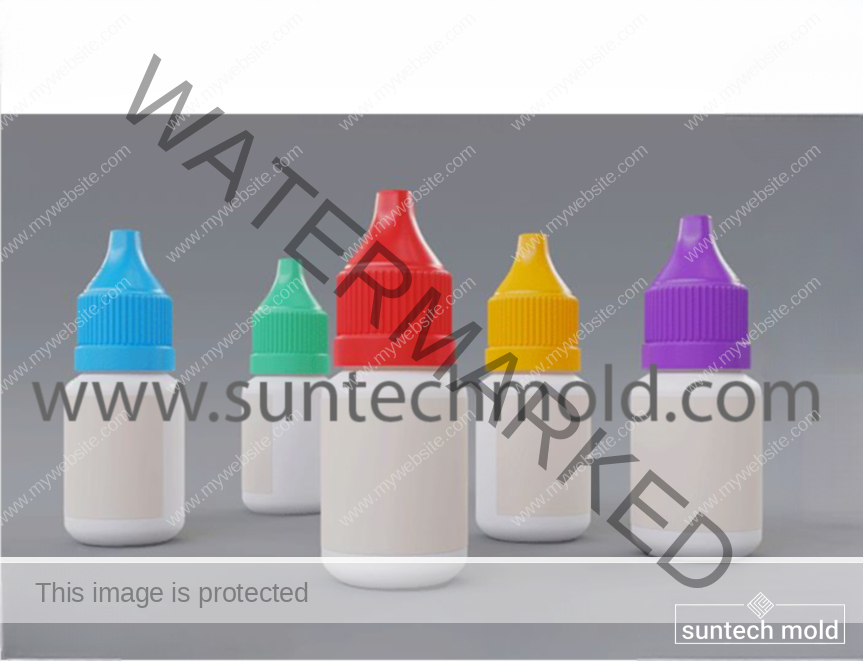
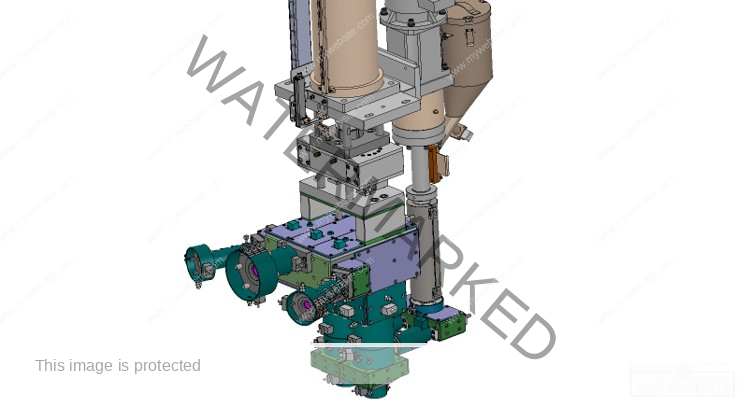
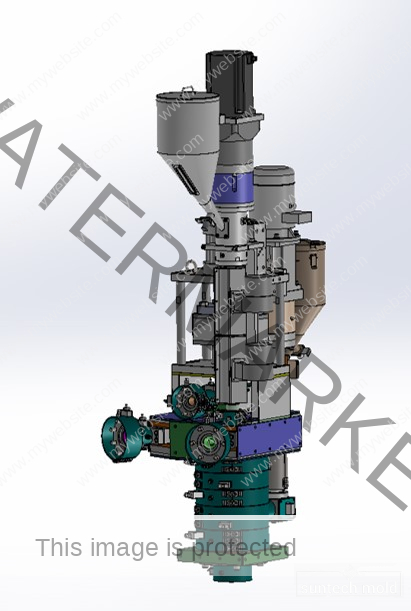
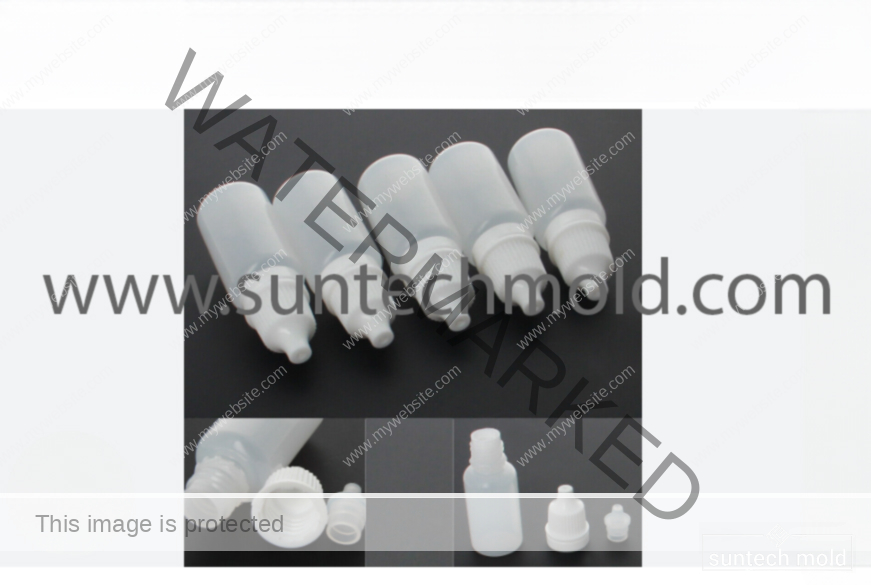
Medical Blow Mold (Suntech)
Choosing the right material for a medical blow mold is a crucial step in the manufacturing process. One key area to focus on is the material used for the cooling channels in the mold. The two most common materials are steel and aluminum, and both have unique features. In this guide, we’ll help you understand which material may be best suited for your medical molding needs.
Understanding Medical Blow Mold Cooling Channels
Why Cooling Channels Matter in Medical Blow Mold
In any mold, cooling channels control the temperature during the forming process. For medical blow mold applications, proper cooling ensures consistent product quality and faster production times. The material you choose for these channels directly affects thermal performance, strength, and durability.
Steel vs. Aluminum in Medical Blow Mold
When selecting between steel and aluminum for a medical blow mold, several key points should be evaluated.
1. Thermal Conductivity
-
Aluminum offers excellent thermal conductivity. This means it transfers heat faster, leading to shorter cycle times.
-
Steel, however, has lower thermal conductivity. This may result in slower cooling, but it can also lead to better control in some cases.
If your production line demands speed, aluminum may offer better efficiency.
2. Weight Considerations
-
Aluminum is lightweight, which can make the mold easier to handle and transport. This is helpful when frequent setup changes are required.
-
Steel is heavier, and while strong, it may be harder to manage manually.
Lighter molds can reduce worker fatigue and improve overall efficiency in a busy production environment.
3. Strength and Durability
-
Steel is more durable and better at handling high stress and pressure. It is ideal for high-stress or long-life applications.
-
Aluminum is still strong, but not as robust as steel under heavy load or impact.
If your medical blow mold will be used in tough conditions, steel may be the more reliable option.
4. Corrosion Resistance
-
Aluminum is naturally resistant to corrosion. Anodized aluminum performs even better in moist or reactive environments.
-
Steel, unless treated, can rust or corrode over time.
For molds exposed to varying conditions or liquids, aluminum is often the safer choice.
5. Machinability and Cost Efficiency
-
Aluminum is easier to machine. This means faster production and less wear on tools, which reduces overall cost.
-
Steel takes more time to machine, often requiring specialized equipment.
Although aluminum is typically more expensive, the savings in time and tooling can balance the overall cost.
6. Application Requirements
Every application is different. When deciding on materials for a medical blow mold, think about the actual use:
-
Choose aluminum for high-speed, high-volume production.
-
Pick steel when the mold needs to last longer or handle more pressure.
Your decision should align with the final product’s requirements.
7. Thermal Expansion
-
Aluminum expands more with heat, which could change the mold shape slightly during production.
-
Steel has lower thermal expansion, so it maintains shape better under heat.
For precise applications, steel offers greater dimensional stability.
8. Flexibility in Design
-
Aluminum is more flexible when creating complex shapes. It allows for creative and efficient cooling channel designs.
-
Steel can be shaped too, but it requires more effort and time.
In applications where design flexibility is needed, aluminum has an edge.
9. Volume of Production
-
Aluminum molds are great for large-volume production due to quick machining and fast cooling.
-
Steel molds suit low-volume, custom, or long-life production needs.
Before choosing, consider how many cycles your medical blow mold will go through over time.
Final Thoughts
The right material for your medical blow mold depends on your specific needs. If speed and corrosion resistance matter most, aluminum may be the right choice. On the other hand, if durability and long-term use are your top concerns, steel might be better.
Every production setup is different. By thinking carefully about thermal conductivity, cost, durability, and design flexibility, you’ll be able to make the best choice for your operation. Whether you choose steel or aluminum, a well-designed medical blow mold will improve your results and save time and money in the long run.