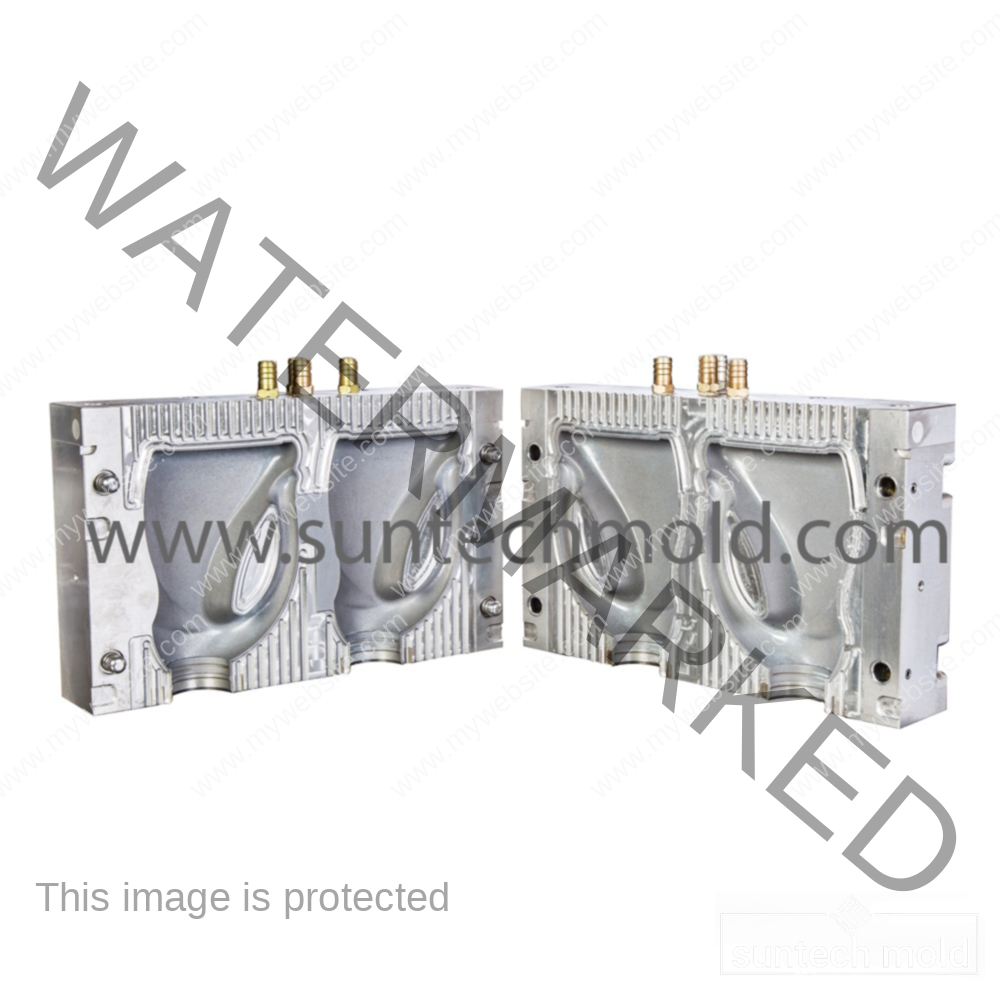
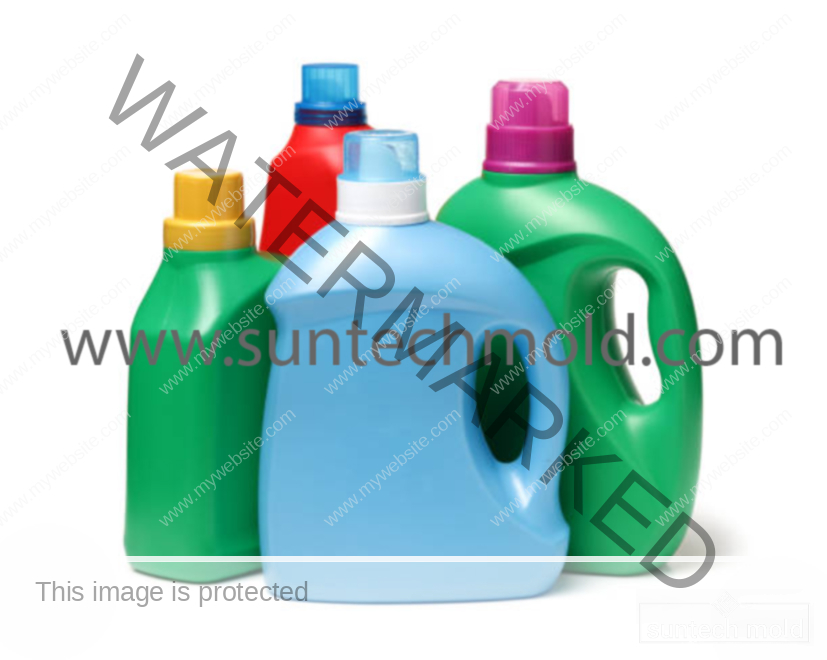
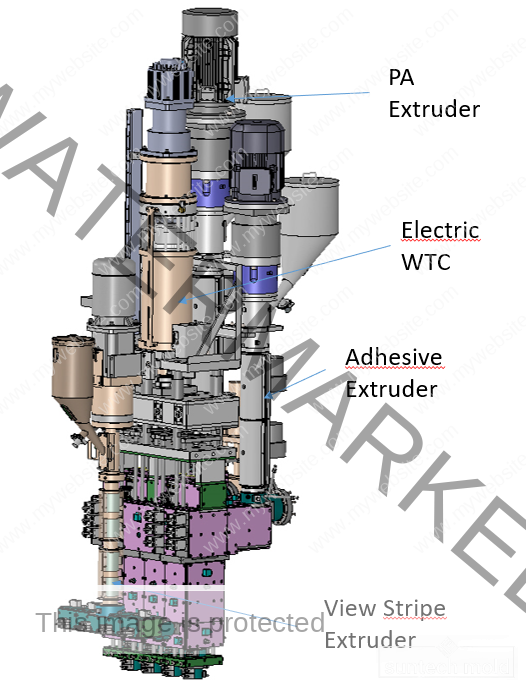
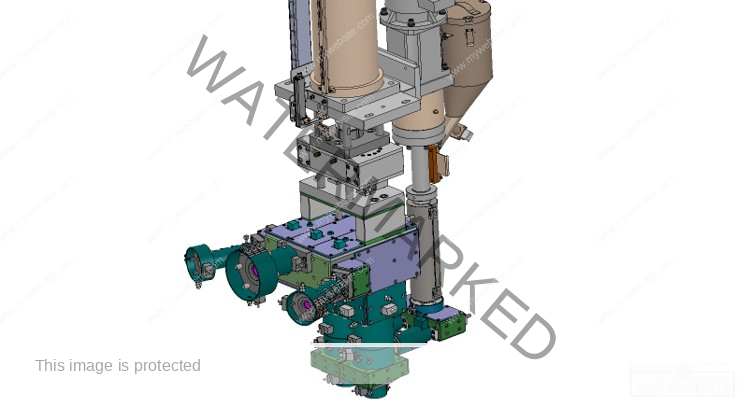
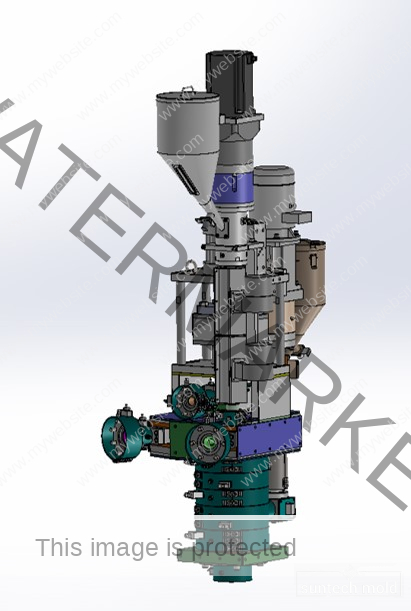
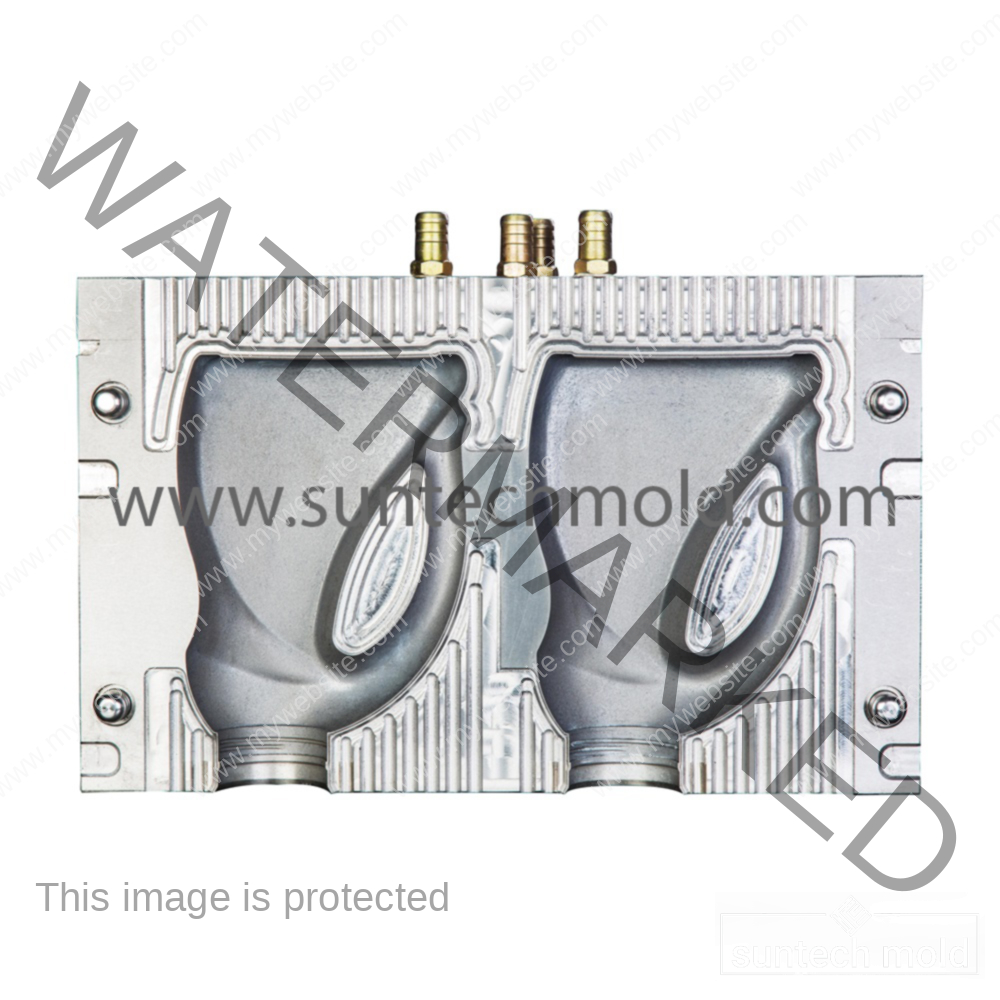
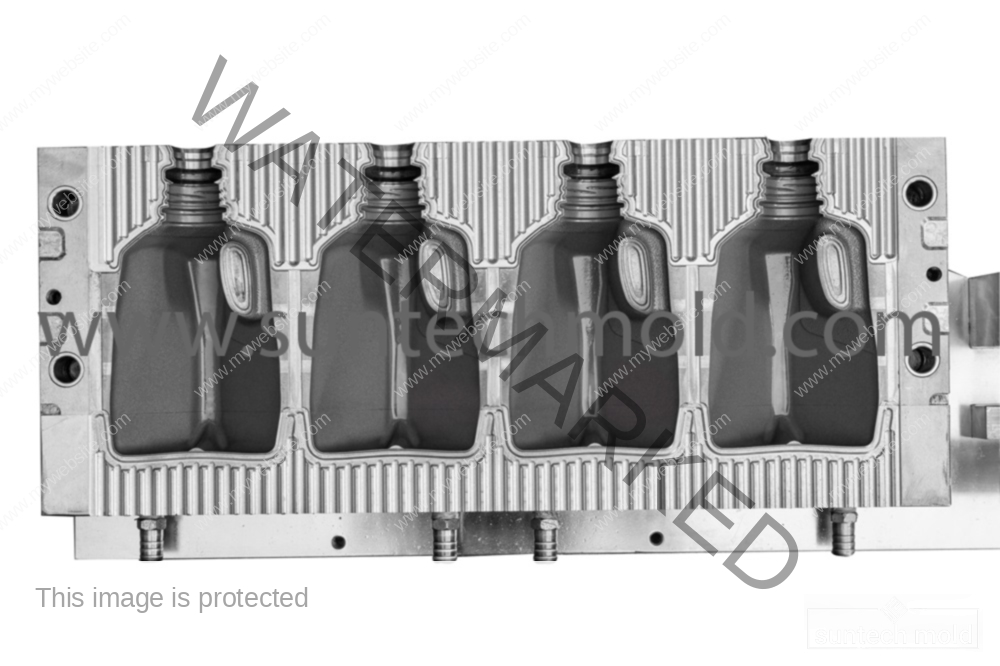
Laundry Detergent Bottle Mold (Suntech)
Creating strong and user-friendly packaging is essential in today’s detergent market. The laundry detergent bottle mold is designed to help manufacturers produce durable, practical, and eco-conscious bottles. However, designing an efficient mold involves more than shaping plastic. It requires careful planning and smart choices across multiple areas—from materials and wall thickness to cooling systems and ejection methods.
In this guide, we will explain the most important design features to consider when selecting or developing a laundry detergent bottle mold for your production needs.
Material Selection for Best Performance
Choosing the right material is one of the most important steps in mold design. The bottle must not only be strong but also safe and recyclable.
1. Type of Plastic
Two popular choices are HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) and PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate). Both offer good chemical resistance and durability. PET provides a clear finish, while HDPE gives a stronger, more opaque bottle. The material must also handle the weight and viscosity of laundry detergent without leaks.
2. Additives and Enhancements
Sometimes, additives like UV stabilizers, colorants, or antimicrobial agents are added. These improve bottle performance, shelf appeal, or hygiene. However, be sure these additives do not interfere with recyclability.
Smart Bottle Design for Everyday Use
While materials are key, the design of the bottle is just as important. A well-designed laundry detergent bottle mold ensures bottles are easy to use and cost-effective to produce.
1. Shape and Size
A bottle should be easy to grip and pour. Rounded edges and contoured sides make handling simpler, especially when the bottle is full. Also, selecting the right volume options (e.g., 1L, 2L, 5L) helps meet different market needs.
2. Neck Design and Closures
The neck must fit various closures such as flip-top caps or measuring caps. Ensuring a precise neck design prevents leaks and improves consumer satisfaction.
Wall Thickness and Structural Strength
A good mold design helps save material while maintaining bottle strength.
1. Consistent Wall Thickness
Bottles with even wall thickness are stronger and use less plastic. This reduces costs and ensures better quality during blow molding.
2. Reinforced Areas
High-pressure points like the handle or base should have extra thickness. These reinforcements help the bottle withstand drops or stacking during shipping.
Mold Design and Efficiency
An efficient laundry detergent bottle mold doesn’t just make bottles—it speeds up your production and cuts waste.
1. Cavity Count
Depending on how many bottles you need to produce, your mold can have multiple cavities. More cavities mean faster output, but they also require higher investment.
2. Cooling System
Faster cooling means quicker cycles. A well-designed cooling system maintains shape and reduces defects while keeping production fast.
Easy Bottle Ejection and Cycle Time
Bottles must be removed quickly and safely after molding to avoid damage or delays.
1. Ejector Pins and Draft Angles
Molds should include smooth ejector mechanisms. At the same time, proper draft angles help bottles release from the mold without sticking or breaking.
2. Shorter Cycle Time
Faster cycles mean more bottles produced per hour. Optimizing mold temperature and airflow can help speed up production while maintaining bottle quality.
Quality Control and Testing
Maintaining quality is vital in packaging. Your laundry detergent bottle mold should include features that make it easier to test and inspect each bottle.
-
Leak testing ensures every bottle is sealed properly
-
Inspection points allow for visual or mechanical checks during production
Environmentally Friendly Design
Today, sustainability is more important than ever. Luckily, the right mold can support green goals.
1. Use of Recycled Plastics
Designing molds that work with recycled materials helps reduce your carbon footprint.
2. Energy-Efficient Production
Molds that cool faster and run on optimized settings reduce energy usage. This helps lower utility costs and emissions.
Compliance and Cost Management
Finally, your mold must meet legal and industry standards while staying cost-efficient.
1. Safety and Labeling
Design your mold to allow space for warning labels, ingredient listings, and barcode placements. These are often required by law.
2. Long-Term Maintenance
A well-designed laundry detergent bottle mold should be easy to maintain. This reduces downtime and repair costs in the long run.
Conclusion
Designing a high-quality laundry detergent bottle mold involves more than shaping plastic. You must carefully balance performance, cost, and sustainability. From selecting the right plastic to designing the bottle for easy use and fast production, each choice affects your success.
By considering material strength, wall thickness, mold cooling, and ejection systems, you can create a mold that produces strong, lightweight, and eco-friendly bottles. In turn, this leads to happy customers and a more efficient factory.
Ready to create your perfect mold? Contact us now to explore custom solutions tailored to your brand and production goals.