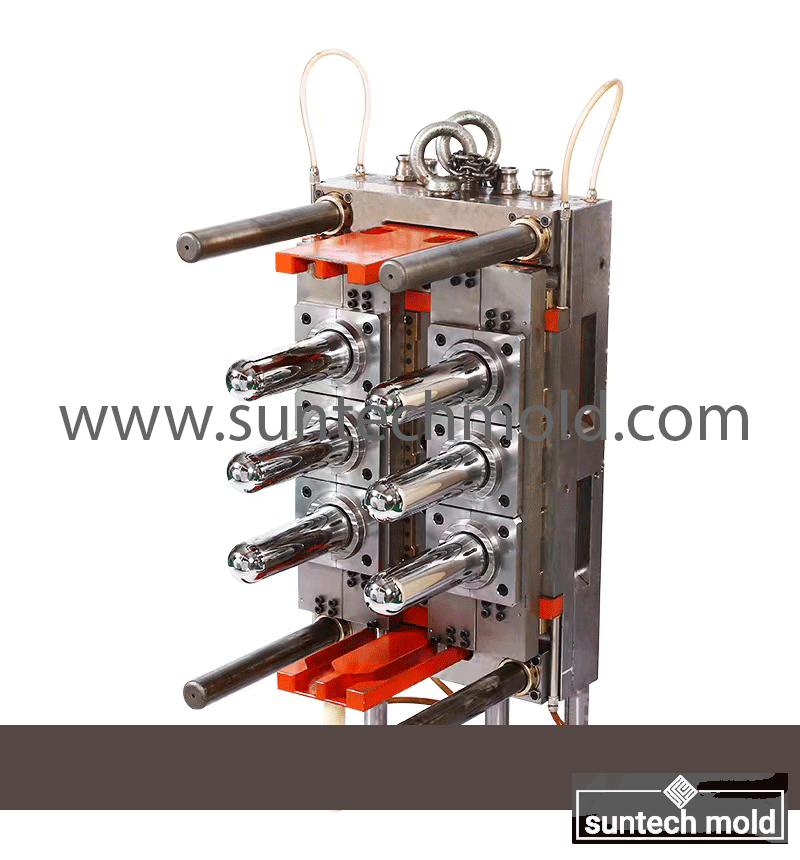
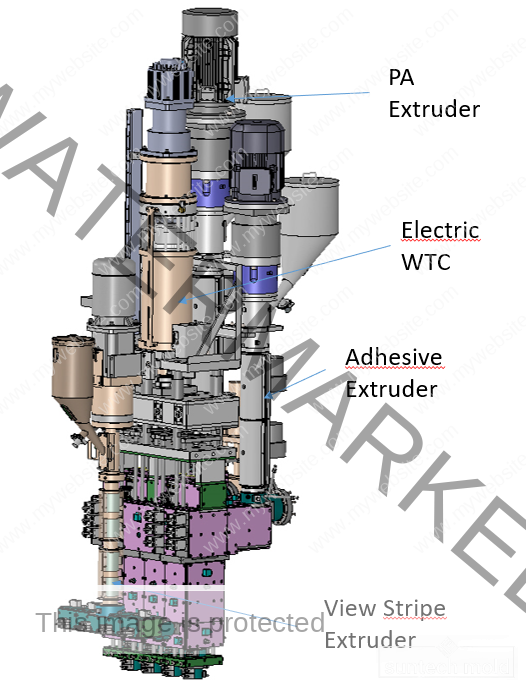
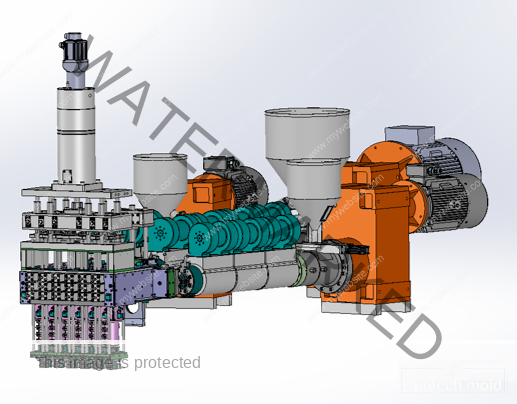
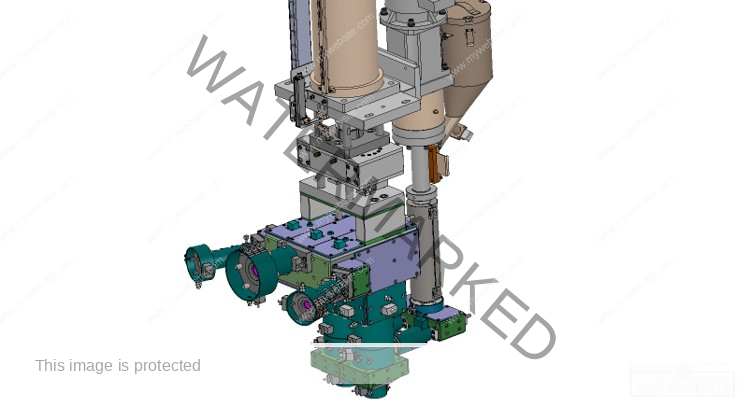
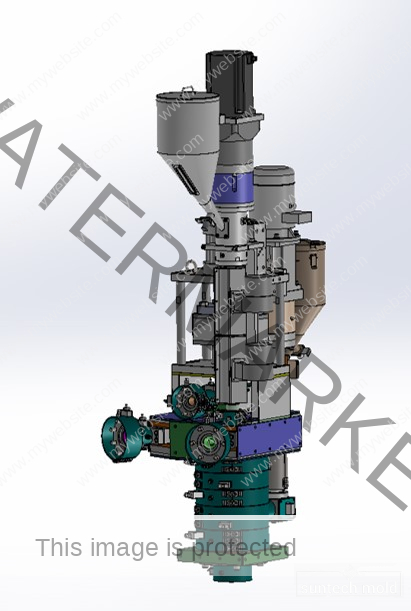
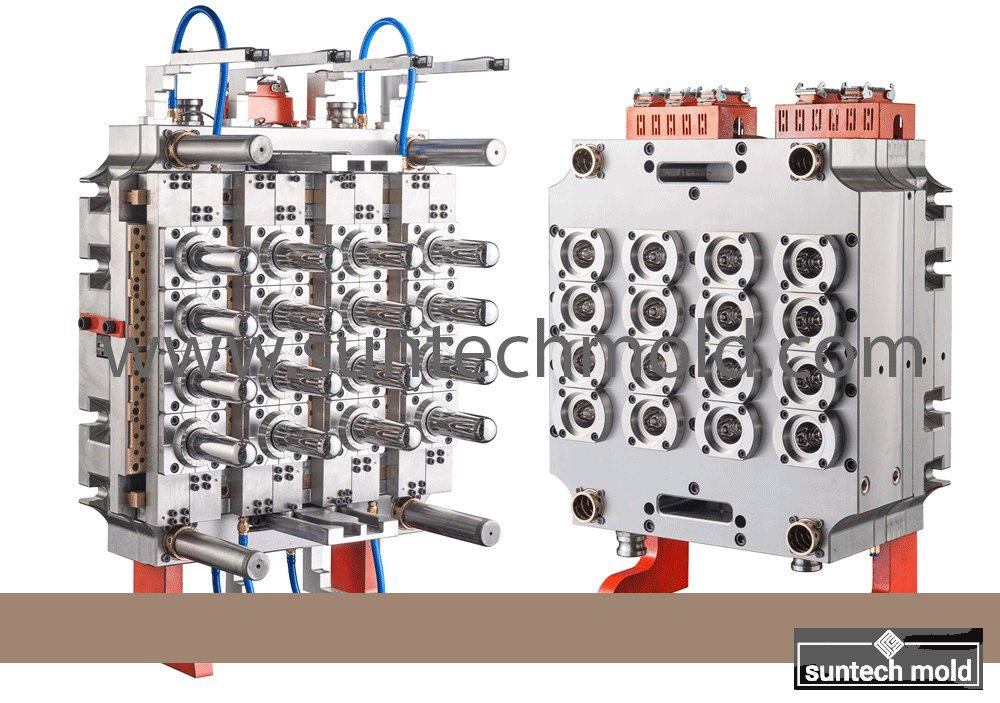
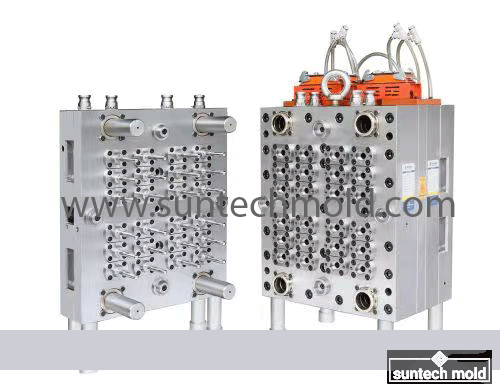
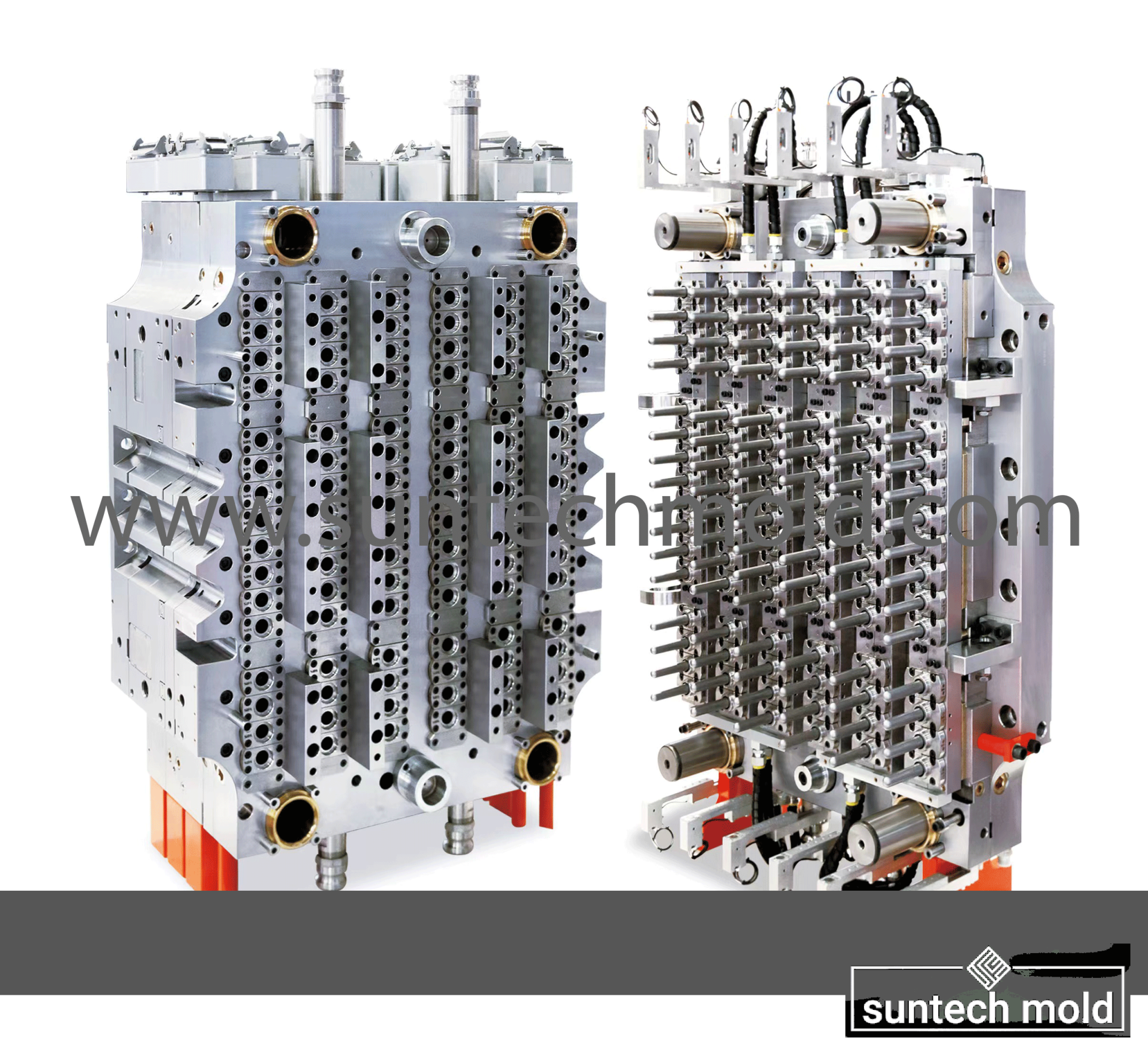
1L Preform Mold – Precision Molding for High-Quality Bottle Production
A 1L preform mold is a vital tool in the PET bottle manufacturing industry, designed to create consistent, high-quality preforms for 1-liter bottles. These molds are typically used in the beverage, household product, and personal care sectors, where uniformity, strength, and clarity are essential. By investing in a precision-engineered 1L preform mold, manufacturers can ensure efficient production, reduced waste, and superior end-product performance.
Defining a good preform mold versus a bad preform mold involves evaluating several key factors. Here are the main considerations:
- Design Accuracy
- Good Mold: Precise design and dimensions that match specifications, ensuring consistent preform quality.
- Bad Mold: Inaccurate dimensions leading to defects in preform size and shape, affecting the final product.
- Material Quality
- Good Mold: Made from high-quality, durable materials that can withstand the pressures and temperatures of the molding process.
- Bad Mold: Inferior materials that wear quickly, leading to defects and reduced lifespan.
- Cooling Efficiency
- Good Mold: Well-designed cooling channels that provide uniform cooling, preventing warping and ensuring consistent cycle times.
- Bad Mold: Inefficient cooling systems that result in uneven cooling, leading to defects and longer cycle times.
- Surface Finish
- Good Mold: Smooth, polished surfaces that promote easy release of preforms and reduce surface defects.
- Bad Mold: Rough or damaged surfaces that cause sticking, leading to defects and increased wear.
- Ejection Mechanism
- Good Mold: Effective ejection systems that cleanly release preforms without damaging them.
- Bad Mold: Inefficient or poorly aligned ejection systems that can cause sticking or damage to preforms.
- Maintenance and Durability
- Good Mold: Designed for easy maintenance, allowing for timely repairs and regular inspections.
- Bad Mold: Difficult to maintain, leading to more frequent breakdowns and reconditioning needs.
- Production Consistency
- Good Mold: Capable of producing consistent preforms with minimal variation, ensuring high-quality output.
- Bad Mold: Produces inconsistent results, leading to higher scrap rates and quality issues.
- Flexibility and Versatility
- Good Mold: Can accommodate different designs and materials, making it adaptable to various production needs.
- Bad Mold: Limited in its application, restricting production capabilities.
Engineered for Consistency and Efficiency
The 1L preform mold is specifically designed to produce PET preforms that will later be blown into 1-liter bottles. These preforms must meet tight dimensional tolerances to ensure compatibility with blow molding machines and filling lines. Precision engineering in the mold’s construction ensures consistent wall thickness, neck dimensions, and material distribution across all cavities.
Key Features of a High-Quality 1L Preform Mold
-
Multi-Cavity Design: Most 1L preform molds come in multi-cavity configurations (such as 4, 8, 12, or 16 cavities), enabling manufacturers to produce multiple preforms per cycle. This increases output and lowers production costs.
-
Hardened Steel Construction: High-grade mold steel with excellent wear resistance is used to ensure long service life and dimensional stability.
-
Optimized Cooling Channels: Efficient cooling systems embedded in the mold reduce cycle times and improve product clarity and finish.
-
Precision Machining: Each cavity is precisely machined to ensure identical preforms, reducing downstream issues during blow molding.
Benefits of Using a Precision 1L Preform Mold
Choosing the right 1L preform mold has a direct impact on operational efficiency and product quality. Some of the major benefits include:
-
Improved Preform Quality: Accurate molding leads to stronger, more uniform preforms with consistent weight and wall thickness.
-
Lower Scrap Rates: With high precision, fewer rejects are produced, reducing waste and saving material costs.
-
Faster Cycle Times: Efficient cooling and ejection mechanisms shorten cycle durations, boosting production output.
-
Longer Mold Life: Durable materials and proper maintenance extend the life of the mold, offering a better return on investment.
Applications in Diverse Industries
The 1L preform is widely used in industries such as:
-
Beverage Bottling: For water, soft drinks, and juices packaged in 1-liter PET bottles.
-
Household Products: Including cleaners, detergents, and fabric softeners.
-
Personal Care: For shampoos, conditioners, and liquid soaps.
Maintenance and Support
To ensure the 1L preform mold operates at peak efficiency, regular maintenance is essential. Lubrication, inspection of wear parts, and cleaning should be part of a routine maintenance schedule. High-end mold suppliers often provide after-sales support, including spare parts, refurbishment services, and technical consultation.
Conclusion
A well-designed 1L preform mold is a cornerstone of efficient PET bottle production. From precision machining and optimized cooling to multi-cavity capabilities, this mold type helps manufacturers achieve consistent quality, faster production, and reduced costs. Investing in the right preform mold ensures a smooth, scalable manufacturing process for 1-liter PET bottles across multiple industries.