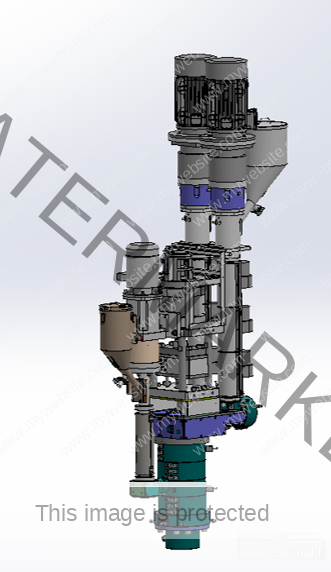
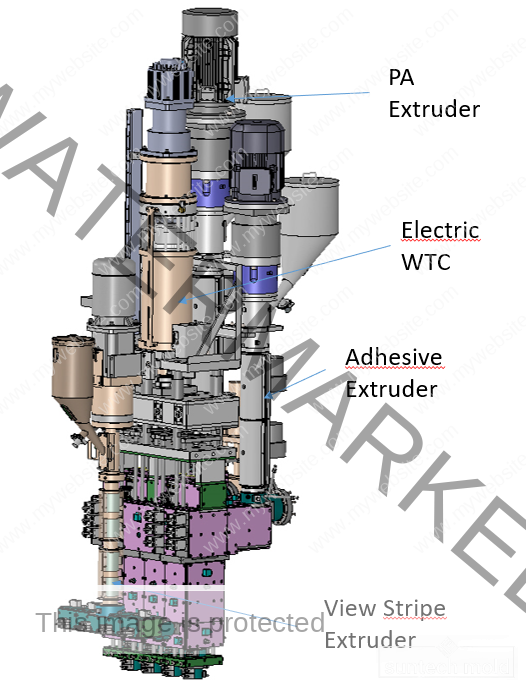
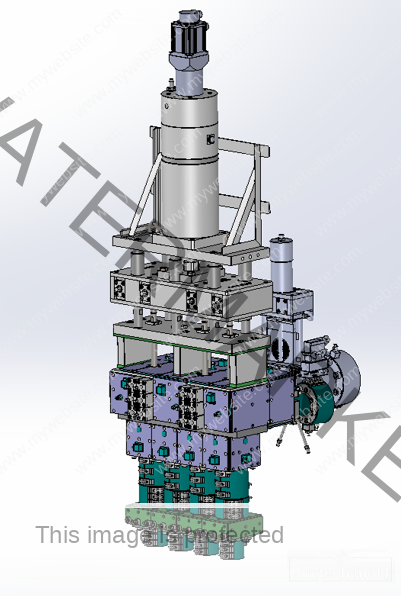
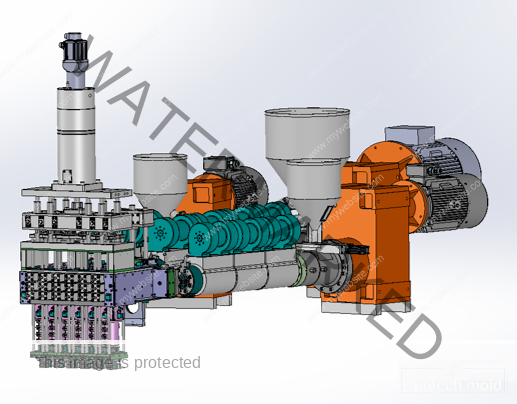
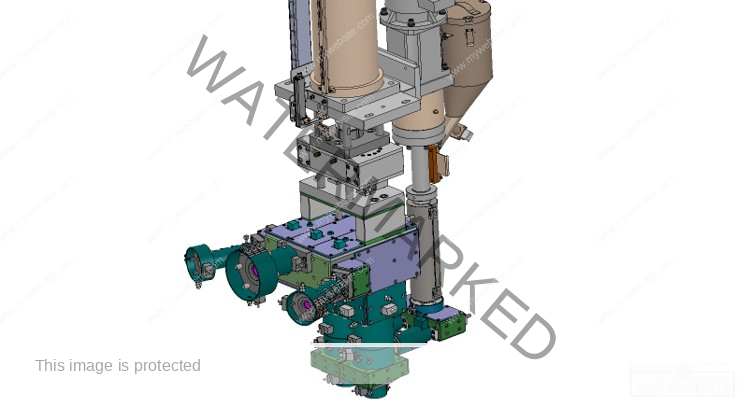
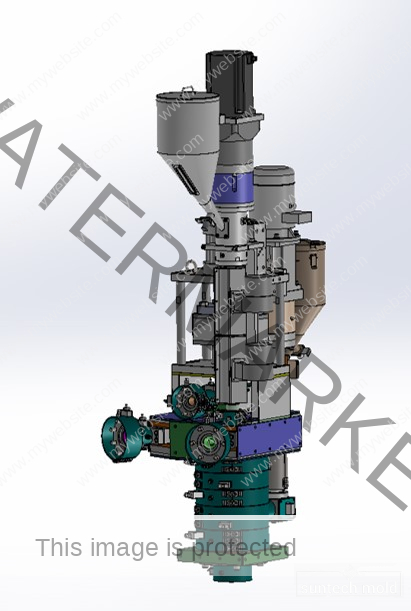
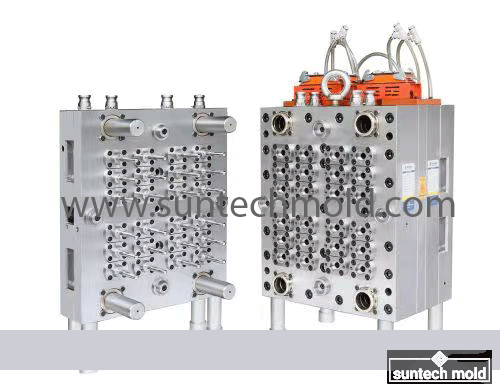
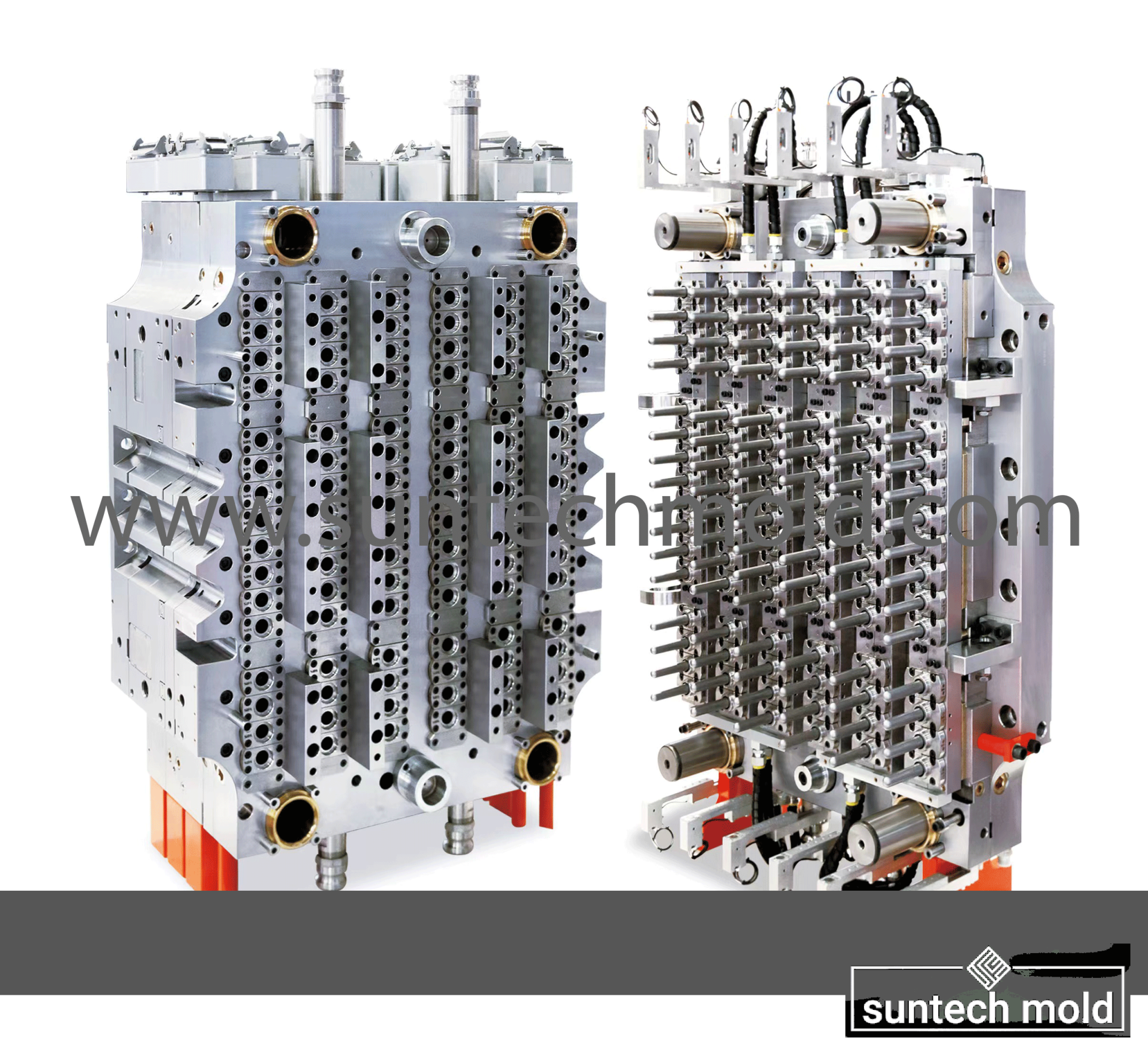
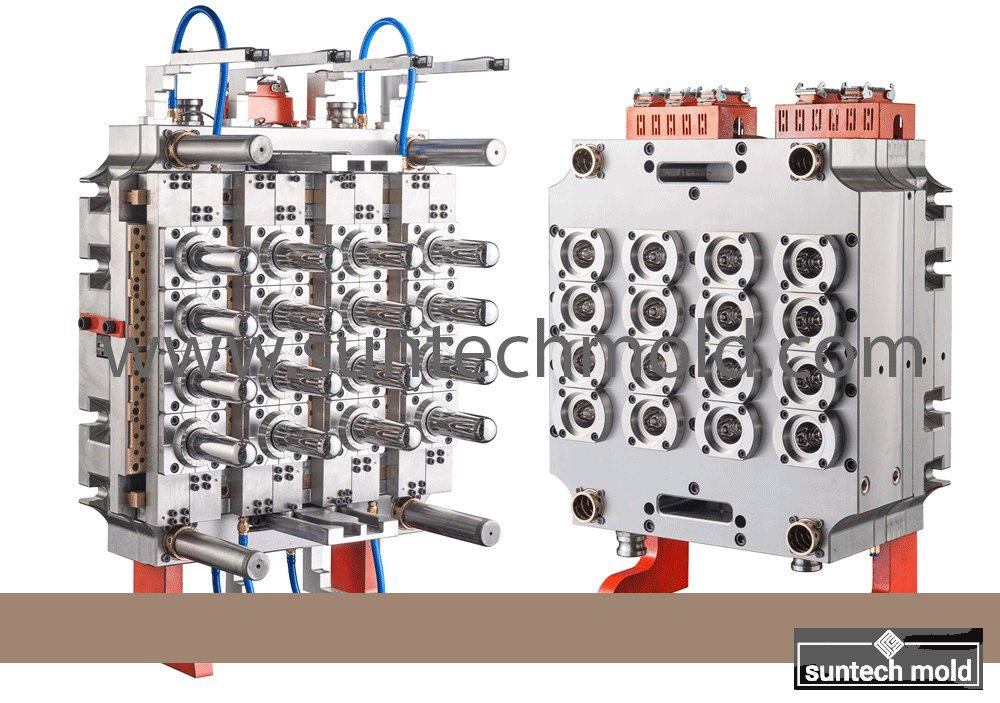
500ml Preform Mold – Precision Molding for Medium-Volume PET Bottles
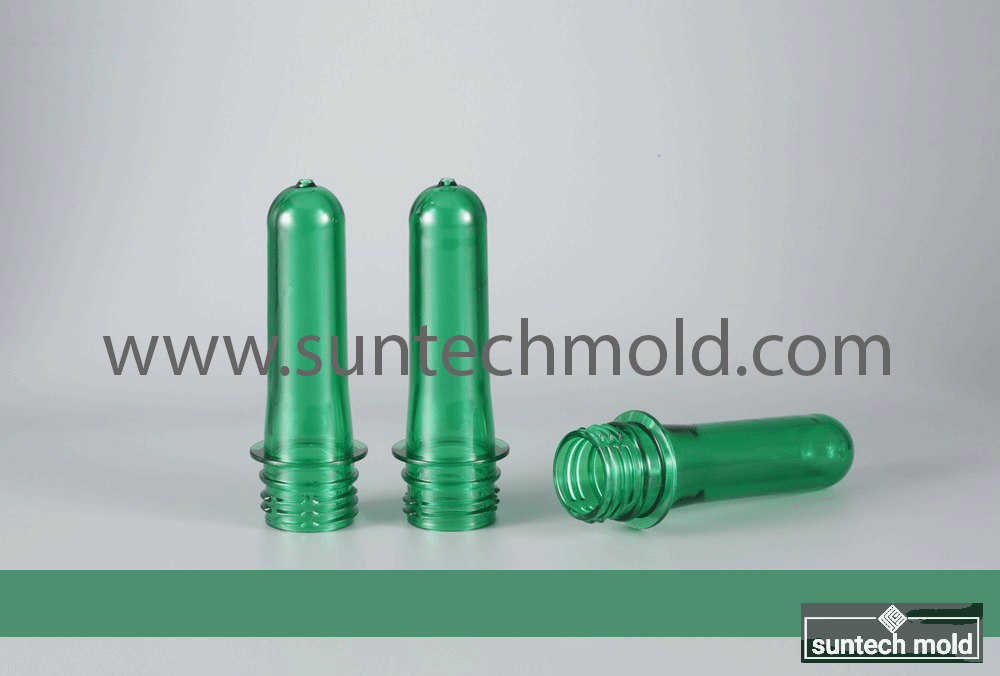
A 500ml preform mold is a vital component in the plastic packaging industry, engineered to produce PET preforms that are later blown into 500ml bottles. These bottles are widely used in industries such as beverages, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and household products. The quality, speed, and precision of the mold directly affect the efficiency of production and the final bottle’s appearance, strength, and consistency.
The design of the mold can significantly influence the selection of resin for the following reasons:
-
Complexity of Mold Design
- Intricate Features: Molds with complex geometries may require resins that flow well and can fill every detail. Low-viscosity resins are often preferred to ensure complete filling.
- Draft Angles: Good draft angles in mold design facilitate easier part removal, which can influence the choice of resin based on its flexibility and shrinkage characteristics.
-
Wall Thickness and Part Design
- Thicker Walls: Parts with thick walls may require resins that have good thermal stability and strength to prevent warping or deformation during cooling.
- Thin Walls: Thin-walled designs may benefit from resins that have fast cycle times and good flow properties, ensuring they can fill the mold quickly.
-
Cooling and Heating Requirements
- Cooling Channels: Effective cooling channel design can impact the resin’s thermal behavior during processing. Resins sensitive to temperature fluctuations may require molds with optimized cooling systems.
- Heating Elements: If the design incorporates heating elements for certain resins, the selection will lean toward those that can withstand higher processing temperatures.
-
Ejection Mechanism
- Ejection Forces: Mold designs that require significant ejection force may influence the selection of tougher, more resilient resins to withstand stress during ejection without cracking.
- Surface Finish: Resins that adhere strongly to mold surfaces may not be suitable if the ejection mechanism relies on smooth release properties.
-
Application Requirements
- Functional Properties: The intended use of the final product can dictate resin selection. For example, if the mold design is for a load-bearing part, strong, impact-resistant resins are necessary.
- Aesthetic Considerations: Molds designed for visually appealing products may require resins that can achieve a high-quality finish or are compatible with coloring agents.
-
Production Volume
- Mass Production: Mold designs intended for high-volume production may favor resins that cure quickly and have predictable shrinkage rates, ensuring consistency.
- Prototype or Low Volume: For lower production runs, more flexible resin options may be acceptable, allowing for easier adjustments in design.
High-Performance Molding for Medium-Size Containers
The 500ml preform mold is designed to strike a balance between production volume and part size. It offers optimal weight distribution, uniform wall thickness, and excellent surface clarity—essential factors for ensuring bottle integrity and customer satisfaction.
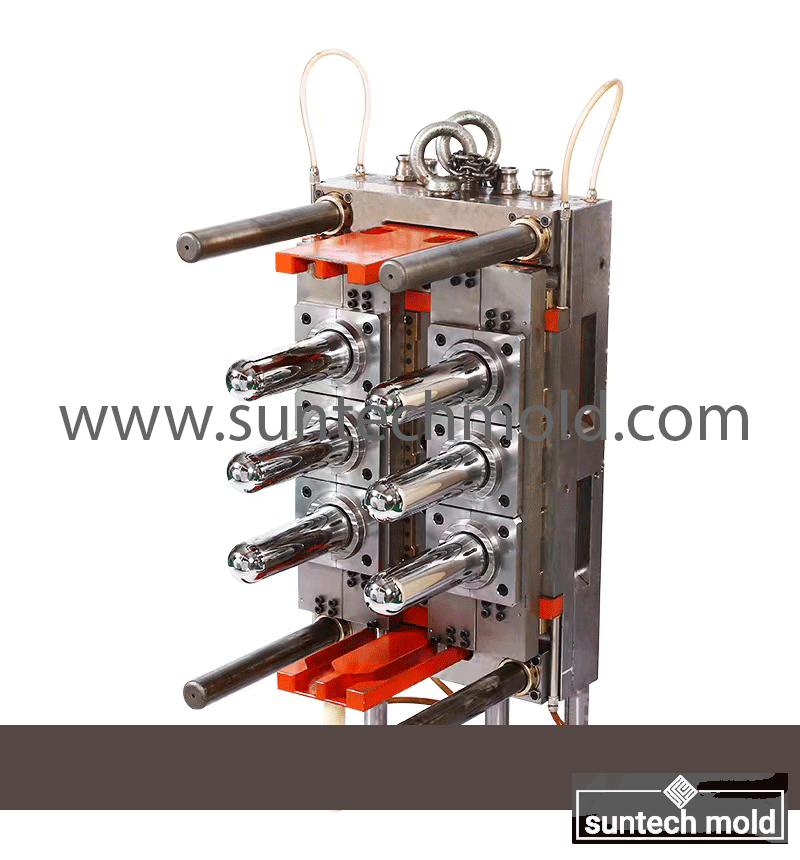
Key Features of the 500ml Preform Mold
-
Multi-Cavity Configuration: Available in a variety of cavity numbers such as 4, 8, 12, 24, or more, the mold can produce multiple preforms per cycle. This supports high-output production lines, maximizing efficiency and reducing cost per unit.
-
Precision Machining: Each mold cavity is CNC-machined to exact tolerances, ensuring dimensional accuracy and compatibility with standard 500ml bottle blow-molding machines.
-
Advanced Cooling Channels: Integrated cooling systems provide faster heat dissipation, helping to reduce cycle time and improve productivity.
-
Durable Construction: Made from high-quality materials like hardened tool steel or stainless steel, the mold resists wear, corrosion, and thermal deformation for long-term, reliable use.
-
Efficient Ejection System: Engineered with ejector pins or plates, the mold ensures smooth removal of preforms, preventing defects or surface blemishes.
Applications Across Industries
The 500ml preform mold is ideal for a wide range of packaging needs, especially where lightweight, easy-to-handle bottles are preferred. Common applications include:
-
Beverage Industry: Used for packaging water, juices, energy drinks, and soft drinks in convenient 500ml sizes.
-
Pharmaceuticals: Suitable for packaging syrups, tonics, and other liquid medications.
-
Personal Care Products: Ideal for shampoos, lotions, conditioners, and body washes.
-
Household and Industrial Liquids: Used for compact detergent, disinfectant, and cleaning solution packaging.
Benefits of Using a High-Quality 500ml Preform Mold
-
Consistency in Preform Quality: Each cavity is optimized for even material flow and cooling, reducing variance in wall thickness or weight.
-
Reduced Production Costs: Fast cycle times and high cavity counts lower overall manufacturing costs per unit.
-
Enhanced Durability: Premium mold materials extend service life, even under high-volume production conditions.
-
Flexibility and Customization: Molds can be customized to specific neck finishes, thread designs, or weight requirements based on client needs.
Conclusion
Mold design has a profound impact on resin selection by influencing flow characteristics, cooling requirements, part complexity, and functional needs. A well-considered mold design can optimize the performance of the chosen resin, leading to better product quality and production efficiency.