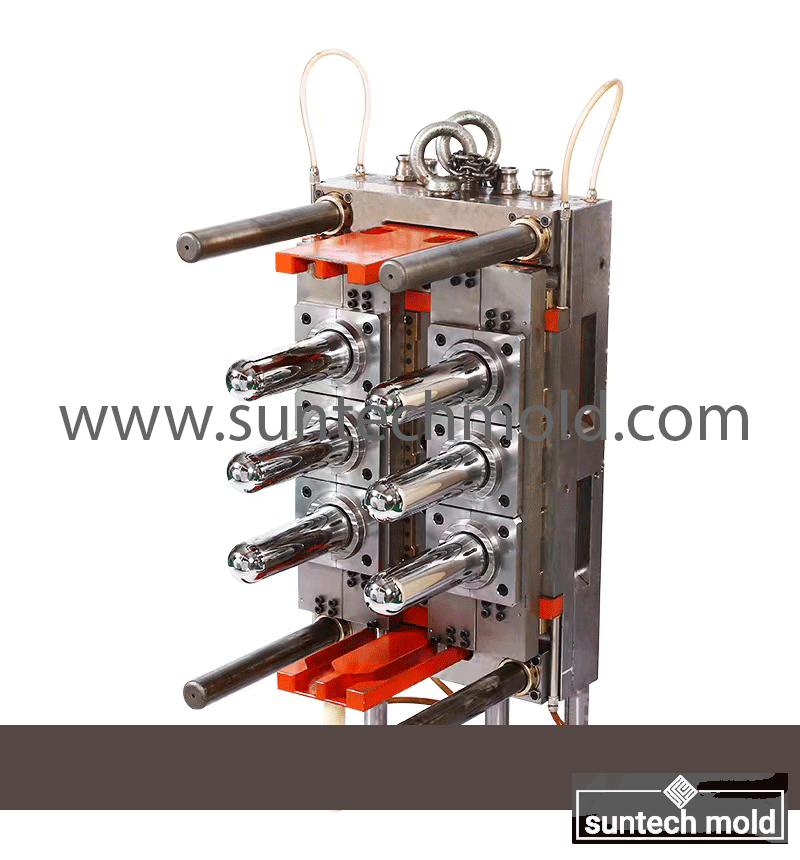
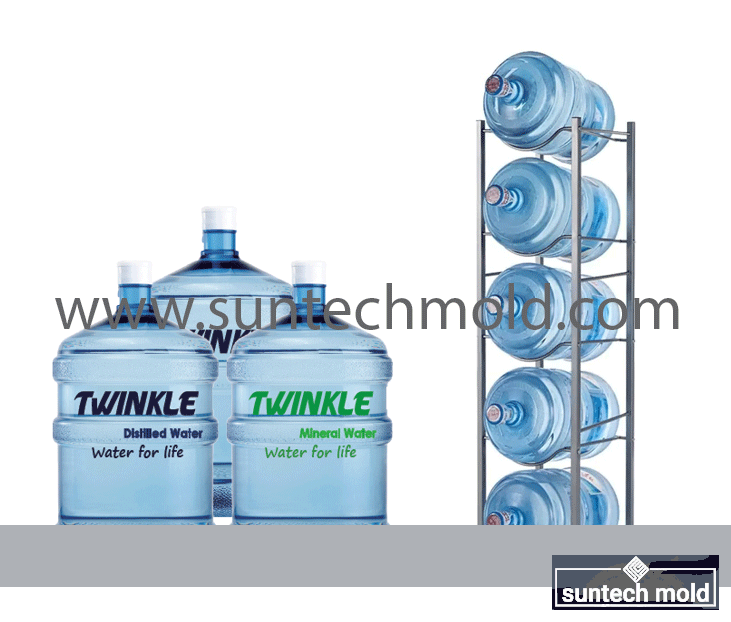
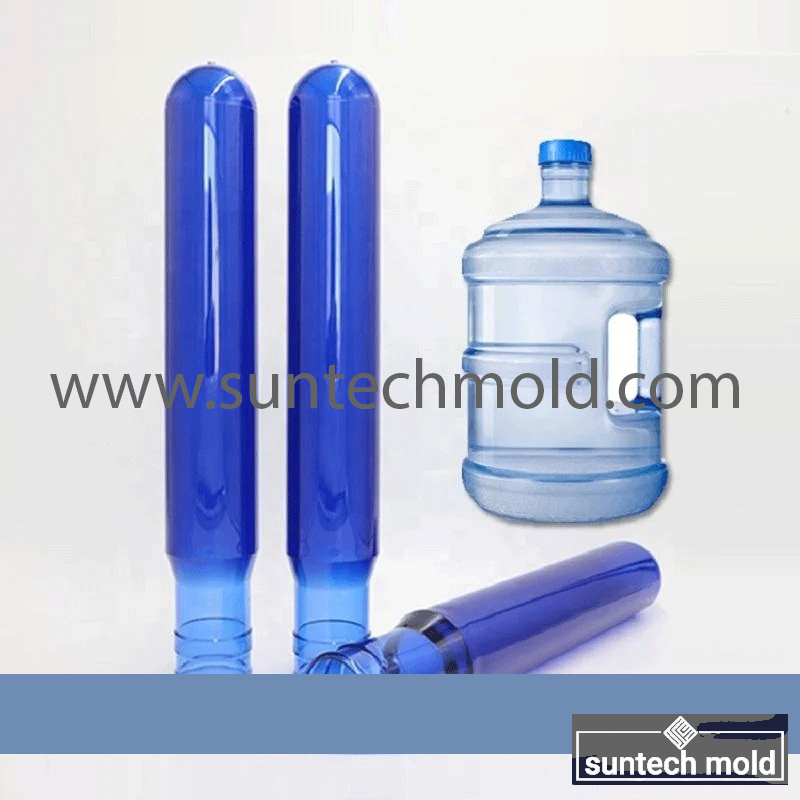
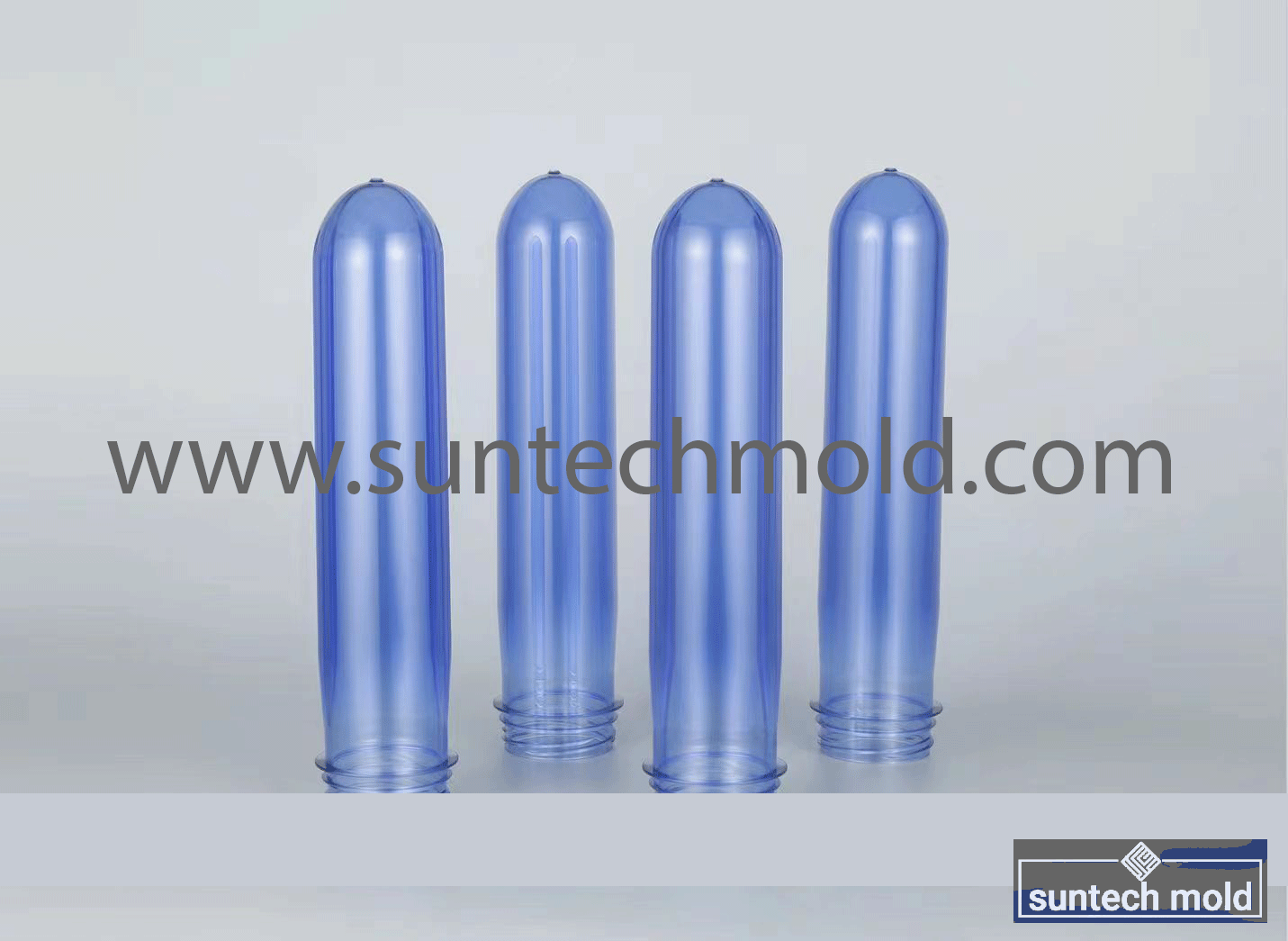
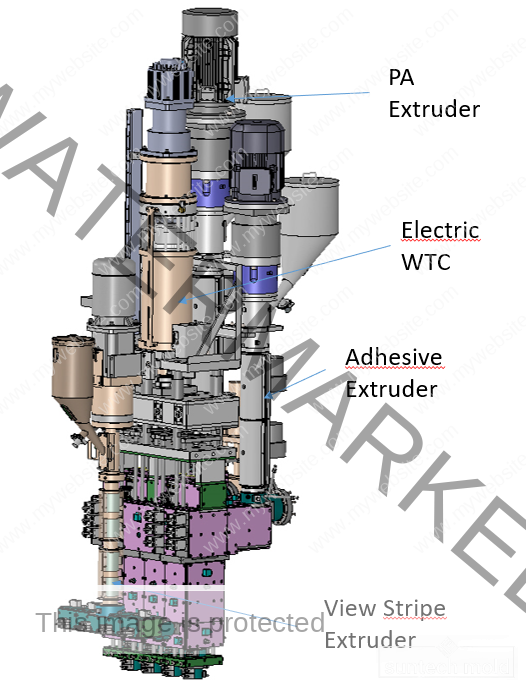
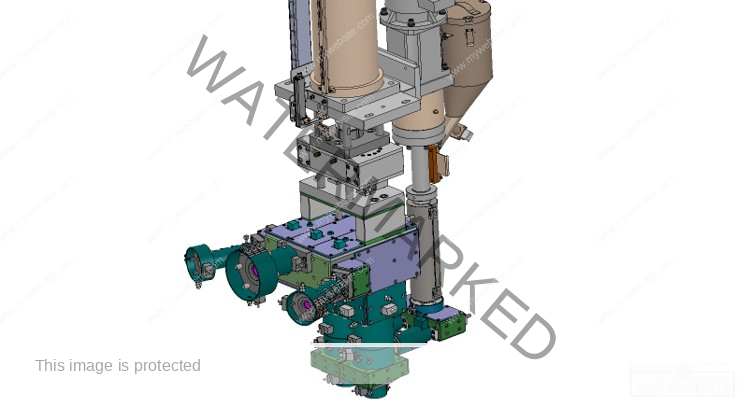
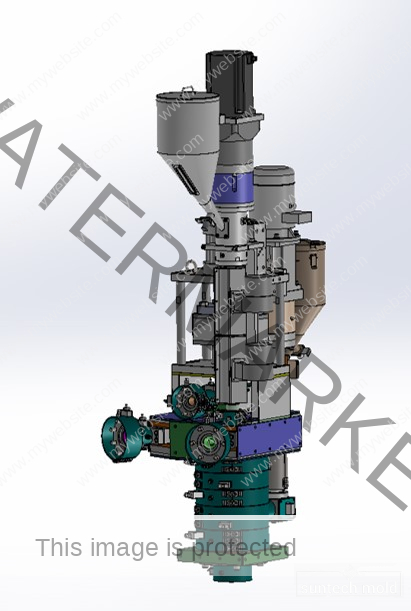
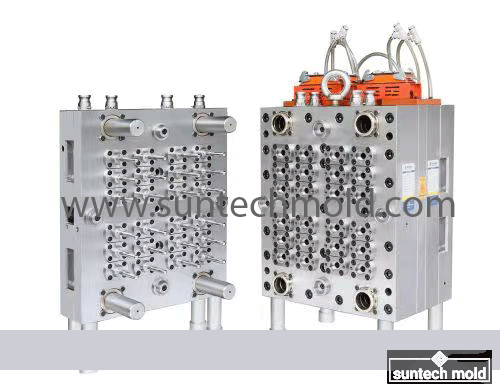
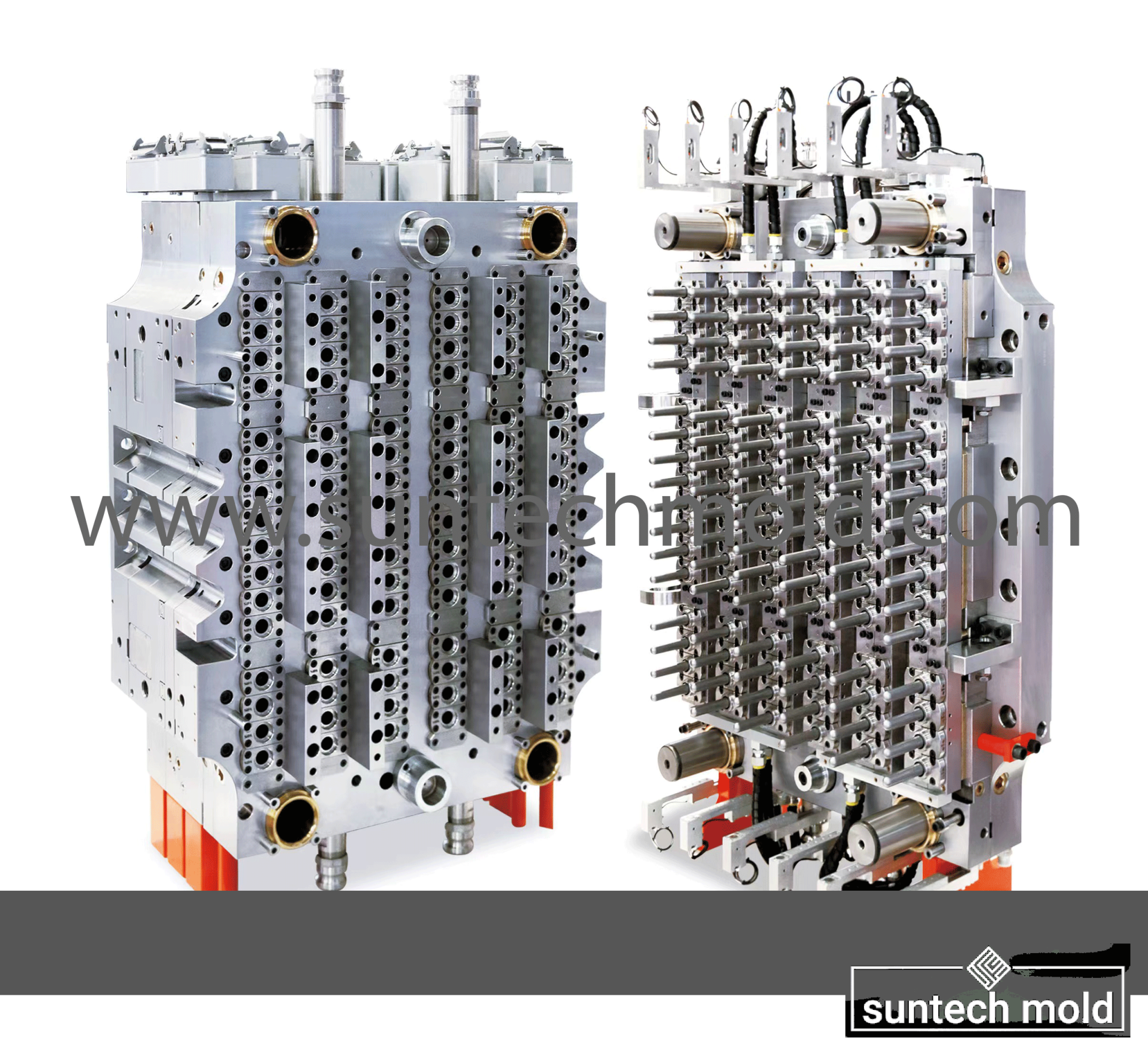
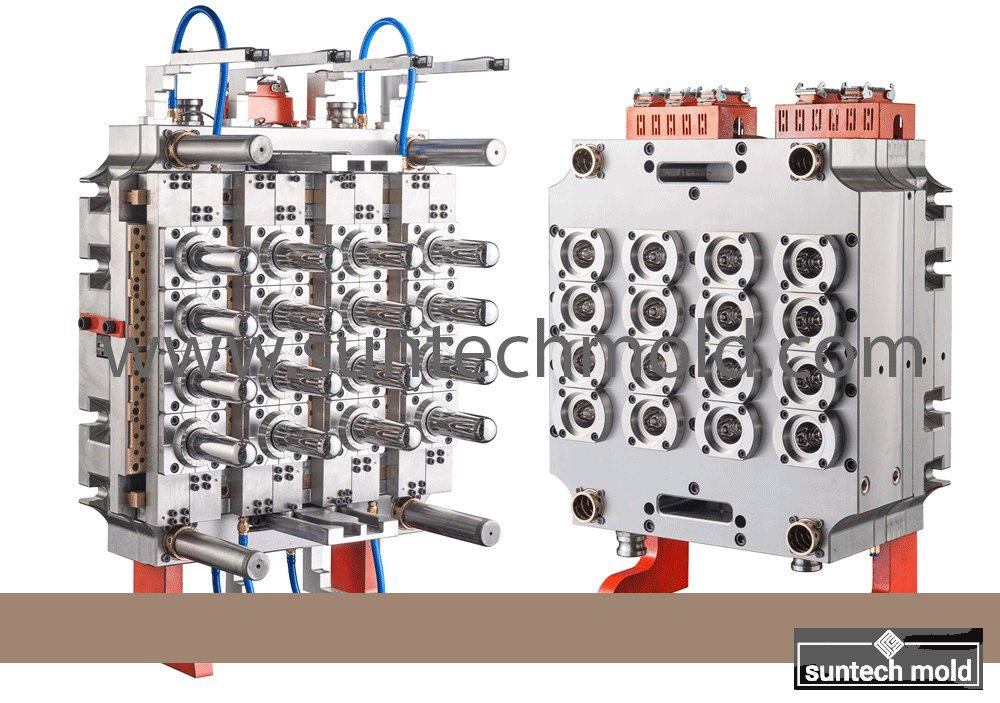
5 Gallon Preform Mold – High-Precision Tooling for Large-Volume PET Containers
A 5 gallon preform mold is a critical tool in the plastic packaging industry, specifically designed to create preforms for 5-gallon PET bottles. These large containers are commonly used for water dispensers, industrial chemicals, and bulk storage solutions. The quality and precision of the preform mold directly impact the strength, clarity, and dimensional accuracy of the final bottle, making it essential to invest in a mold that ensures consistent performance and durability.
Material Selection for Preform Molds
Choosing the right material for preform molds is crucial for ensuring durability, performance, and cost-effectiveness. Here are the common materials used, along with their advantages and typical applications:
- Tool Steel
- Types: H13, D2, A2
- Advantages:
- High hardness and wear resistance
- Excellent dimensional stability
- Good toughness and thermal conductivity
- Applications: Ideal for high-volume production and complex geometries.
- Aluminum Alloys
- Types: 7075, 6061
- Advantages:
- Lightweight and easy to machine
- Good thermal conductivity, aiding in cooling
- Cost-effective for low to medium production runs
- Applications: Often used for prototype molds or short production runs.
- Stainless Steel
- Advantages:
- Excellent corrosion resistance
- Good strength and durability
- Applications: Suitable for molds exposed to harsh environments or moisture.
- Copper and Copper Alloys
- Advantages:
- Superior thermal conductivity
- Effective for heat dissipation
- Applications: Often used in molds requiring efficient cooling, such as high-speed injection molding.
- Bimetallic Materials
- Advantages:
- Combines properties of two metals for enhanced performance
- High wear resistance with good thermal management
- Applications: Used in high-demand applications where mold longevity is critical.
- Plastics (Specialty Thermoplastics)
- Advantages:
- Lightweight and corrosion-resistant
- Suitable for low-volume applications
- Applications: Used in specialized or prototype situations.
Considerations for Material Selection
- Production Volume: High-volume applications may benefit from durable materials like tool steel, while low-volume runs might use aluminum.
- Thermal Management: Materials with good thermal conductivity can improve cycle times and product quality.
- Cost: Balance between initial material cost and long-term performance and maintenance.
- Type of Resin: Compatibility with the type of resin being used can affect mold performance and durability.
- Surface Finish Requirements: Certain materials allow for smoother finishes, impacting the final product quality.
Engineered for High-Volume, Heavy-Duty Production
Producing 5-gallon PET bottles requires precision tooling capable of handling thick walls, long cooling cycles, and demanding material flow characteristics. A well-designed 5 gallon preform mold supports these requirements with high-performance features and robust construction.
Key Design Features of the 5 Gallon Preform Mold
-
Thick-Walled Cavity Design: Due to the size of 5-gallon containers, the mold must be capable of producing thicker preforms without compromising clarity or structural integrity.
-
Advanced Cooling Channels: Efficient thermal management is essential to prevent warping and to reduce cycle times, especially when molding large, heavy preforms.
-
Strong Ejection Systems: With heavier preforms, powerful and precise ejection mechanisms are needed to remove the part cleanly and without damage.
-
High-Precision Machining: Each cavity must be machined to exact tolerances to ensure uniform weight and wall thickness across all preforms, which is crucial for blow molding consistency.
Materials and Construction for Long-Term Performance
A 5 gallon preform mold is typically constructed from premium materials like hardened tool steel or stainless steel for maximum durability and wear resistance. In some advanced designs, copper alloys may be incorporated to enhance thermal conductivity and speed up cooling.
-
Tool Steel (H13, S136): Offers excellent strength, heat resistance, and dimensional stability under high pressure and temperature.
-
Stainless Steel: Used where corrosion resistance is important, especially in food-grade water bottle applications.
-
Copper Inserts: Improve thermal transfer in areas where faster cooling is required, helping maintain product clarity and reduce cycle time.
Customization and Cavity Options
Depending on production needs, a 5 gallon preform mold may be configured as a single-cavity or multi-cavity system. While single-cavity molds are ideal for lower production volumes or prototyping, multi-cavity molds allow manufacturers to scale production efficiently.
Applications and Industries
The 5 gallon preform mold is widely used in:
-
Bottled Water Industry: For 18.9L / 5-gallon water dispenser bottles.
-
Chemical Packaging: Where large, durable containers are needed for safe transport and storage.
-
Food and Beverage: In bulk syrup, oil, and ingredient storage.
Conclusion: Reliable Performance for Demanding Packaging Needs
The 5 gallon preform mold is a vital asset for manufacturers producing large PET containers. With the right mold, companies benefit from improved efficiency, reduced production defects, and enhanced final product quality. Whether you’re entering large-volume packaging or upgrading existing systems, choosing a precision-engineered mold ensures long-term success and reliability in your production line.