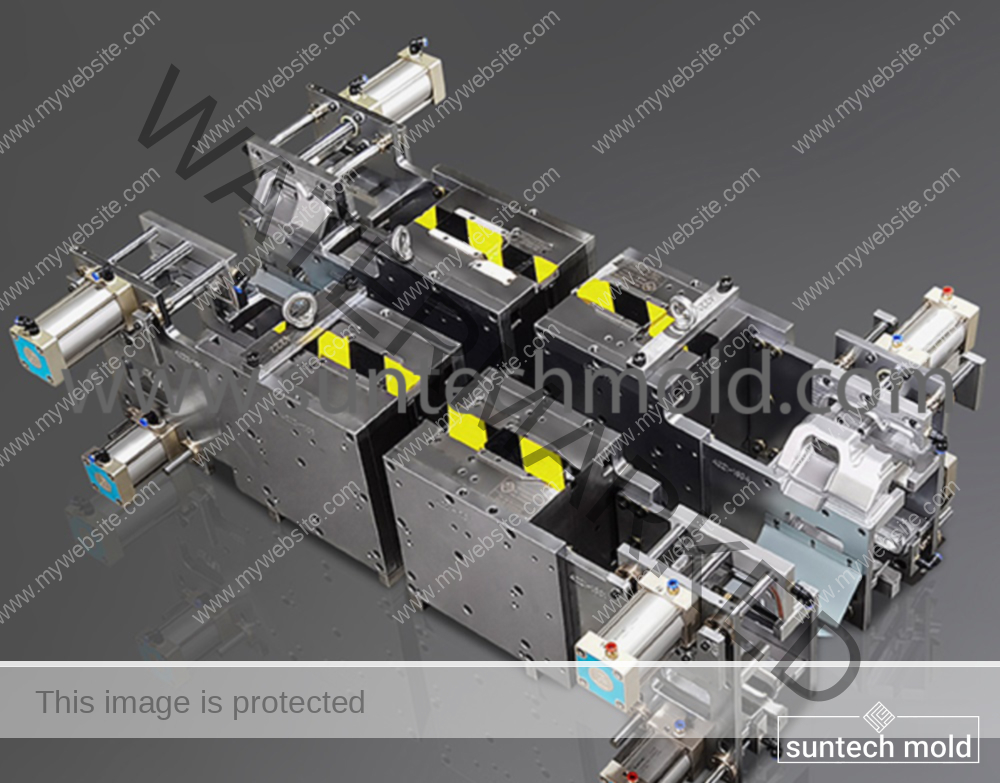
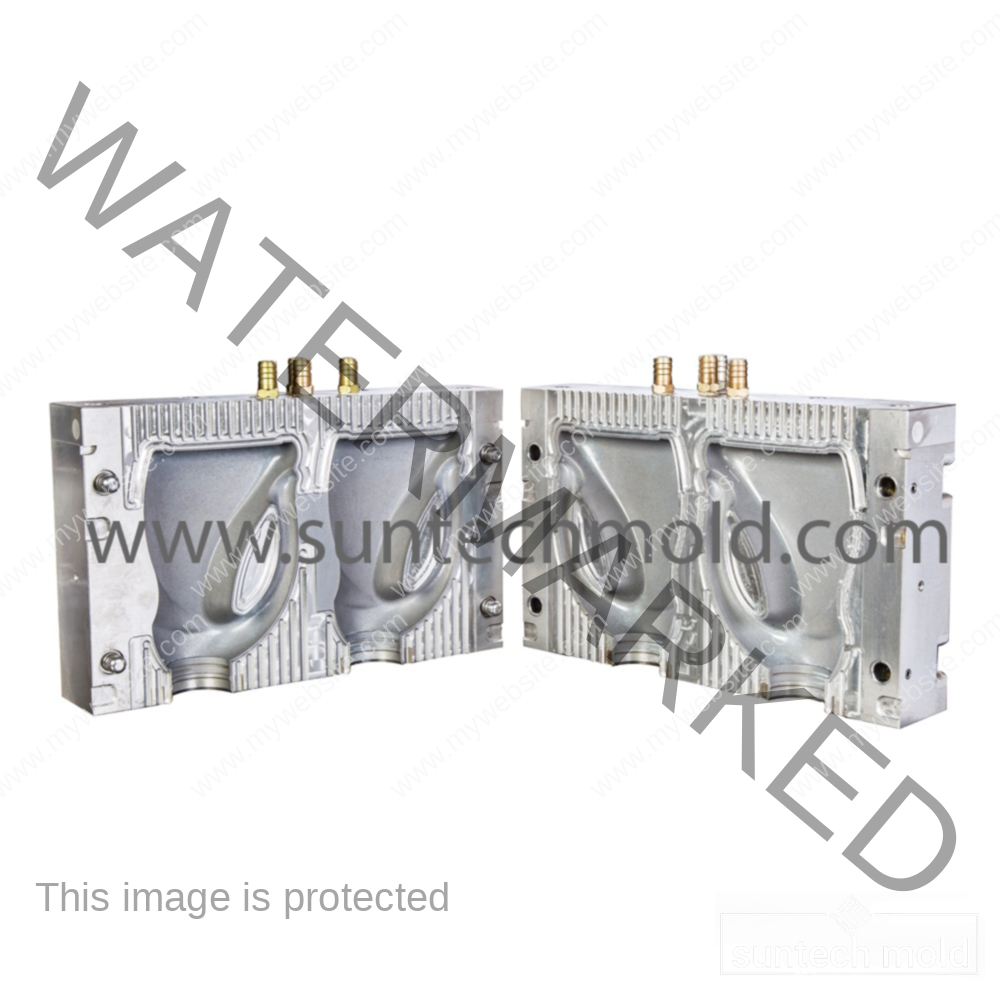
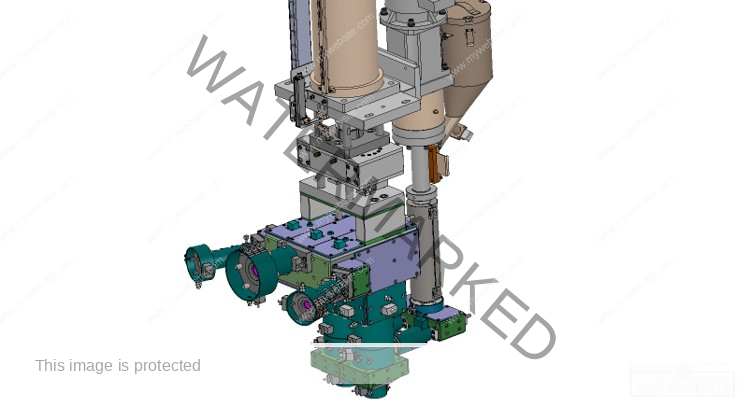
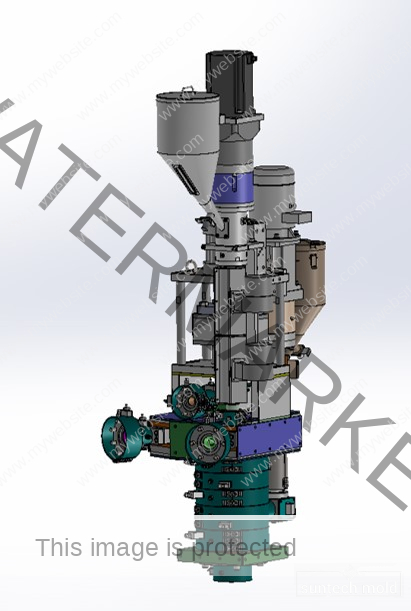
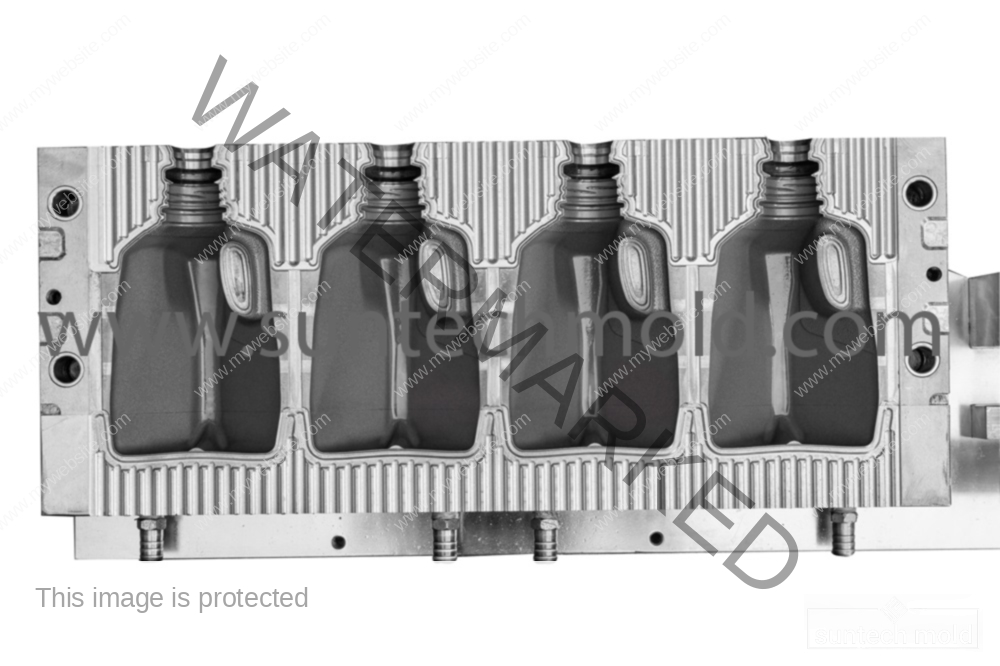
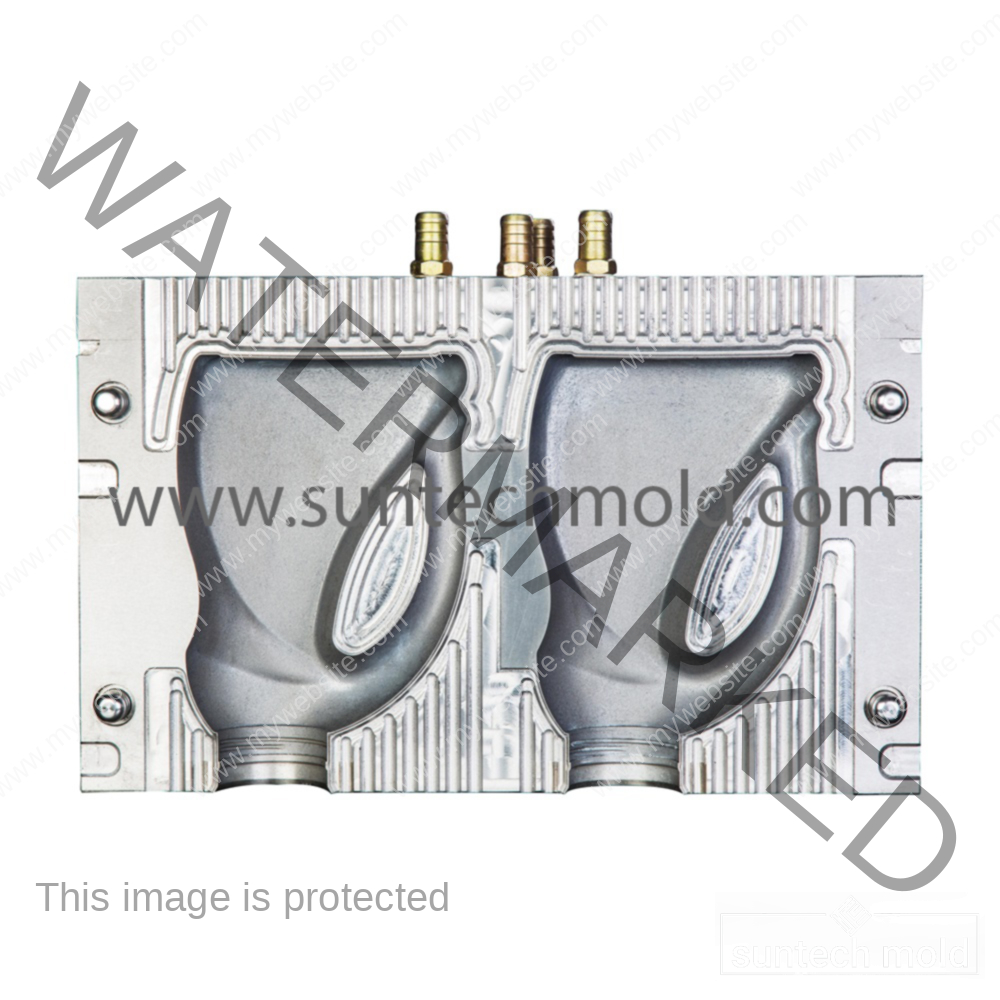
Fabric Softener Mold (Suntech)
Are you looking for a reliable and eco-friendly way to produce fabric softener bottles? The fabric softener mold is the perfect tool for creating high-quality, durable bottles in various shapes and sizes. Whether you’re a small manufacturer or a large-scale producer, choosing the right mold is the first step toward better production, less waste, and a cleaner future.
In this guide, we will explore how this mold works and what to consider when choosing between extrusion and injection blow molding methods.
Why the Right Fabric Softener Mold Matters
Choosing the right fabric softener mold is more than just picking a shape. It affects your production speed, product quality, and environmental footprint. From material waste to water usage, the manufacturing process you use can make a big difference.
But before selecting a mold, it’s important to understand how different blow molding processes impact the environment.
Environmental Impact of Blow Molding Methods
There are two common methods used for making plastic bottles: extrusion blow molding and injection blow molding. Both methods have pros and cons. Let’s look at how they compare in terms of sustainability and performance.
Material Waste
One of the biggest differences between the two processes is how much plastic waste they generate.
-
Extrusion blow molding creates more scrap during the parison (tube) stage. It also needs trimming, which adds to waste.
-
In contrast, injection blow molding uses material more efficiently. Since the preform is shaped more precisely, there’s less leftover plastic.
Reducing waste not only saves money but also helps protect the environment.
Energy Consumption
Energy use is another important factor when selecting your fabric softener mold process.
-
Extrusion blow molding can use more energy because the machine runs continuously. But it may still be cost-effective for large-volume production.
-
Injection blow molding uses more energy per cycle since it involves two steps. However, for smaller batches, it might consume less energy overall.
So, if your production size is small, injection molding could be the greener choice.
Recyclability of Products
When it comes to recycling, using the right materials and molding method matters.
-
Extrusion blow molding can handle recyclable materials, but sometimes different plastics are combined, making recycling harder.
-
Injection blow molding, however, usually works with single-material preforms. This makes the bottles easier to recycle.
As more consumers care about recycling, this is something worth thinking about.
Emissions and Water Use
Environmental protection also means looking at air and water.
Emissions
-
Extrusion blow molding often operates at higher temperatures and for longer cycles. This can lead to more volatile organic compounds (VOCs) being released.
-
On the other hand, injection blow molding offers more control over heat and timing, which helps lower emissions.
Water Usage
Both processes use water to cool down the bottles after forming. However:
-
Extrusion blow molding may require more water because it runs longer.
-
Injection blow molding uses shorter cycles, so it often needs less water.
Lower water use means less environmental stress, especially in areas where water is limited.
Transportation and Lifecycle Impact
When you look at the full lifecycle of a bottle made using a fabric softener mold, it’s also important to consider size and weight.
-
Extrusion blow molding is often used for larger bottles, which may take up more space during transport. This can increase the carbon footprint.
-
Injection blow molding tends to create smaller, lighter bottles. As a result, transportation becomes more efficient, and emissions can be reduced.
Even small changes in size or weight can lead to big savings over time.
Making the Sustainable Choice
So, which process should you choose for your fabric softener mold? It depends on your needs:
-
If you need high-speed production and simple shapes, extrusion blow molding might be best.
-
If you’re producing smaller bottles with a focus on quality and recycling, injection blow molding could be the smarter option.
In either case, using recycled materials and improving energy efficiency can make your entire production process more eco-friendly.
Final Thoughts
To sum up, the fabric softener mold is an essential part of bottle manufacturing, and choosing the right process plays a key role in both performance and sustainability. Whether you go with extrusion or injection blow molding, you can reduce waste, lower energy costs, and create products that are easier to recycle.
With the right mold and a smart approach to production, your business can grow while helping protect the planet.
Contact us today to get a custom quote or learn more about our eco-friendly mold options.